* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Shunt Pathway Significance of pentose phosphate pathway
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Free-radical theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
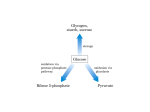
Hexose Monophosphate ( HMP ) Shunt Pathway
Normally , 10% of glucose is metabolized through this pathway which operates in
the cytoplasm . Energy ( ATP ) is not generated nor required .
Significance of pentose phosphate pathway :
This pathway has two main functions :
A - The major metabolic role of the pathway is the generation of reduced
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate ( NADPH ) .
B - Generation of ribose-5-p necessary for the biosynthesis of nucleotides ,
nucleotide coenzymes and nucleic acids .
Reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway :
The pathway has two phases :
1 - oxidative irreversible phase .
2 - non-oxidative reversible phase .
1 - The oxidative irreversible reactions :
● In the oxidative irreversible reactions , one carbon of glucose-6-p is released as
CO2 , two NADPH are generated and the remaining carbons form ribulose-5-P
( a pentose phosphate , 5 C ) . The enzyme glucose-6-P dehydrogenase( GPD ) is
the rate-limiting enzyme .
2 - The non-oxidative reversible reactions :
■ Ribulose-5-p may be isomerized to ribose-5-p ( a pentose phosphate ) or
epimerized to xylulose-5-p ( pentose phosphate ) .
■ Transfer & rearrangement of carbon atoms between Ribose & Xylulose
( catalyzed by the enzymes Transketolase & Transaldolase ) ultimately form
Fructose-6-p & Glyceraldehydes-3-p .
Functions of NADPH :
1 - NADPH is used for reductive biosynthesis particularly of fatty acids ,cholesterol
and steroid hormones .
2 - NADPH has bactericidal role :
During inflammation , bacteria phagocytosed by inflammatory cells ( neutrophils ,
eosinophils , monocytes and macrophages ) . These cells contain the enzyme NADPH
Oxidase that produce superoxide anion from oxygen which requires NADPH . The
superoxide anion is converted to hydrogen peroxide and then to hypochlorous acid
(HClO) by the enzymes Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) & Myeloperoxidase ( MPO ) .
The superoxide & hypochlorous ions are the final effectors of bactericidal action .
This is a deliberate production of free radicals by the body . About 10% of oxygen
uptake by macrophages is used for free radical generation .
Regulation of pentose phosphate pathway :
1 . The oxidative phase of the pathway is controlled by the level of NADP+ ; it can only
proceed if NADPH is oxidized back to NADP+ .
2. The rate-limiting enzyme Glucose–6–P Dehydrogenase ( GPD ) is inhibited by high
NADPH level .
3. The non-oxidative phase is controlled by the requirement of the cell to ribose .
Glucose-6-p dehydrogenase ( GPD ) deficiency :
● Is the most common genetic enzyme deficiency .
● These patients cannot generate enough NADPH by the pentose phosphate pathway
necessary for antioxidant system to defend erythrocytes against reactive
oxygen species .
● Individuals with this genetic deficiency have attacks of severe hemolytic anemia and
jaundice when taking certain drugs like anti-malarial drugs primaquine and sulfa
drugs { condition called drug-induced hemolytic anemia } or after ingestion of broad
beans , , {condition called Favisim } .
● Erythrocytes in GPD-deficient individuals still have the defense mechanisms
provided by the antioxidants vitamins E & C and the enzyme catalase . Thus
these patients remain asymptomatic unless the oxidant-antioxidant balance is
disturbed by taking drugs or ingesting broad beans that shifts the balance towards
increase in oxidants relative to antioxidants and which leads to oxidative stress
situation causing RBC destruction and lyses .
***********************************