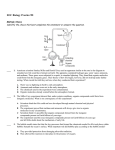
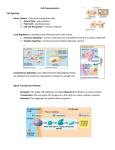
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Test MC and answers - Bremen High School District 228
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup