* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The anterior pattern of the mesoderm is key for the next phase of
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
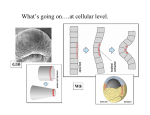
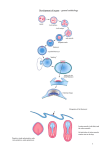
10/12/09 The anterior pattern of the mesoderm is key for the next phase of development: somitogenesis After mesoderm ingression, medial/lateral patterning establishes distinct mesodermal domains somites somites notochord lateral plate mesoderm Distinct mesoderm domains give rise to specific derivatives: thus, in mesoderm, axes, and then position equals fate Eomes acts as an early and essential determinant of extraembryonic and pre-somitic mesoderm Sequential gene expression determines the presomitic mesoderm Mutation of different Tbox genes gives rise to distinct mesodermal phenotypes brachyuryTbx6 Tbx6-/- phenotype) brachyury -/- (“T” phenotype) 1 10/12/09 Somitic mesodermal identity is lost in Tbx6 mutant Additional mutations that compromise somite formation Include multiple members of the notch signaling pathway Somitic mesoderm is converted to neural tube-like structures Notch signaling relies upon cell-cell contact, and is modulated by several feedback mechanisms * * ** ** ** * Feedback regulation of Notch and Notch ligands regulates neighbor distinctions among cells Periodicity of somitogenesis, and temporal variation in expression of notch pathway molecules suggests that Notch signaling establishes somite boundaries 2 10/12/09 Dynamic expression of Notch pathway genes in “split embryo” prerparations shows oscillatory behavior of gene expression at transcriptional level Fix Culture Fix Oscllations are intrinsic to somitogenic mesoderm: they do not rely on surrounding mesodermal, ectodermal, or endodermal tissues Culture unlikely due to cell movement Notch target genes in presomitic mesoderm cells have intrinisic oscilliatory expression Differential adhesion and morphogenesis follow oscilliatory gene expression and signaling Mutations in Hes7 (Hes genes are transcriptional effectors of Notch signaling) disrupt downstream regulation of genes that influence somitogenesis A model for oscillatory signaling that divides the presomitic mesoderm into somites in a spatially and temporally ordered manner from anterior to posterior 3 10/12/09 1. Anterior expression domain of Mesp2 identifies next somite’s anterior boundary 2. Activated (NICD) notch and Lfng oscillate in register with Mesp2 3. Mesp2 regulates Notch activation via Delta regulation 4. Mesp2 protein oscillates to set posterior and anterior domains of Notch activation and thus define somite boundaries 3. Regulation of NICD via Lnfg is disrupted in Mesp2 null 4. Mesp2 and NICD positively regulate Lnfg, and Hes7 provides negative feedback; the Mesp2 regulation of Lnfg may be direct 4 10/12/09 5. A model for the role of Mesp2 in regulating Notch activity via Dll1, Lnfg and Hes7 5