* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
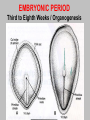
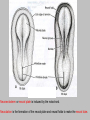
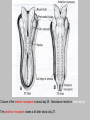
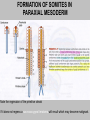
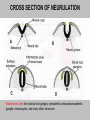
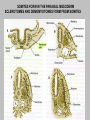
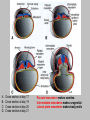
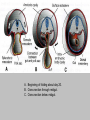
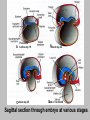
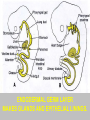
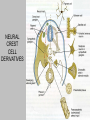
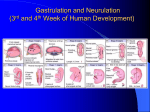
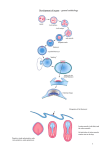
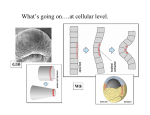
EMBRYONIC PERIOD Third to Eighth Weeks / Organogenesis Neuroectoderm or neural plate is induced by the notochord. Neurulation is the formation of the neural plate and neural folds to make the neural tube. Closure of the anterior neuropore is about day 25. Nonclosure results in anencephaly. The posterior neuropore closes a bit later about day 27. Anencephaly has a frequency of 0.3 per 1000 in the United States. It has slight predominance for females. There is little cerebral tissue: the diencephalon is present, hence the eyes. FORMATION OF SOMITES IN PARAXIAL MESODERM Note the regression of the primitive streak If it does not regress a sacrococcygeal teratoma will result which may become malignant. A sacrococcygeal teratoma is the result of failure of primitive streak regression. In the United States the occurrence is about 1 in 40,000 live births. Teratomas from any origin are benign tumors that arise from germ cells. They may contain a variety of structures such as skin, neurons, glands, and cartilage. These may be seen grossly or microscopically. The tissues are not organized. 90% of sacrococcygeal teratomas up to 2 months are benign. However, half of them diagnosed later in life are malignant. CROSS SECTION OF NEURULATION Neural crest cells form dorsal root ganglia, sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia, melanocytes, and many other structures. SOMITES FORM IN THE PARAXIAL MESODERM SCLEROTOMES AND DEMOMYOTOMES FORM FROM SOMITES FORMATION OF VERTEBRAE Somites in the paraxial mesoderm will give rise to sclerotomes. Anterior (A) designates toward the head. Posterior (B) is caudal. The caudal part of the sclerotome above will invade the cranial part of the below. Note that a vertebral body is made of a P and an A. P A A. B. C. D. Cross section at day 17 Cross section at day 19 Cross section at day 20 Cross section at day 21 Paraxial mesoderm makes somites. Intermediate mesoderm makes urogenital. Lateral plate mesoderm makes body walls A. Beginning of folding about day 20. B. Cross section through midgut. C. Cross section below midgut. Presomite before day 19 about day 25 about day 22 end of 1st month Sagittal section through embryo at various stages. ENDODERMAL GERM LAYER MAKES GLANDS AND EPITHELIAL LININGS. NEURAL CREST CELL DERIVATIVES