* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
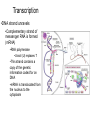
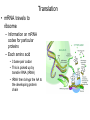
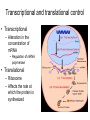
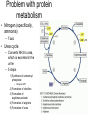
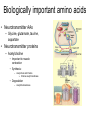
Protein metabolism Roles of proteins • DNA – Only codes for proteins • Proteins – Structure and shape – Metabolic capability Amino Acids • Building blocks of proteins • 20 in the human body • Contain C,H,O and Nitrogen • Contain – Amine group • NH2 – Carboxyl group • COOH • Also contain a side chain – Makes amino acids different Amino acids • These make up the 20 AAs in the body – Essential • Necessary in the diet – Non-essential • Can be manufactured – Meat vs vegetarian diet Protein structure and function • Proteins – Made up of AAs – Synthesized in the ribosome – Control: DNA & RNA • Chromosomes – Genetic information – Contains codes for protein synthesis • DNA – Pentose sugar (deoxyribose) – Phosphate group – Organic base (purines; A and G and pyrimidines; T and C) • A,T,G,C • Thymine binds Adenine and Cytosine binds guanine – Parallel strands that run in opposite directions Transcription •DNA strand unravels •Complementary strand of messenger RNA is formed (mRNA) •RNA polymerase •Uracil (U) replaces T •This strand contains a copy of the genetic information coded for on DNA •mRNA is translocated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm Translation • mRNA travels to ribsome – Information on mRNA codes for particular proteins – Each amino acid • 3 base pair codon • This is picked up by transfer RNA (tRNA) • tRNA then brings the AA to the developing protein chain Transcriptional and translational control • Transcriptional – Alteration in the concentration of mRNA • Regulation of mRNA polymerase • Translational – Ribosome – Affects the rate at which the protein is synthesized Amino acid metabolism • No excess protein storage in body – Excess is converted to fat or sugar or oxidized – Protein turnover is very high • Repair and maintenance • Enzymes – Rapid turnover allows them to adapt quickly to changing demands – E.g. rise and fall in oxidative enzyme activities with training and detraining • Turnover – Balance between synthesis and degradation Amino Acid metabolism • Transamination – When the amine group of an amino acid is transferred to another molecule • This molecule is typically a keto acid – Essentially an AA without a nitrogen group Deamination • Glutamate dehydrogenase – Along with the coenzyme NAD+ (Glutamate) • Deaminates glutamine to alphaketoglutarate • Produces ammonia (Glutamate) Transamination • Serum glutamatepyruvate transaminase (SGPT) (glutamate) – Transfers nitrogen from Glutamate to pyruvate which is transaminated to alanine (glutamate) Protein metabolism in exercise • Oxidation – Muscle can only oxidize the following AAs • Alanine, aspartate, glutamate, leucine, isoleucine, valine – BCAA » L, I and V » Most important – However, oxidation accounts for only ~ 5-10% of energetic needs Problem with protein metabolism • Nitrogen (specifically, ammonia) – Toxic • Urea cycle – Converts NH3 to urea, which is excreted in the urine – 5 steps 1) Synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate – Requires ATP 2) Formation of citrulline 3) Formation of argininosuccinate 4) Formation of arginine 5) Formation of urea Gluconeogenesis • Some AAs are glucogenic (red), some ketogenic (yellow) • Some also function to help maintain the Kreb’s cycle (anaplerotic additions) Biologically important amino acids • Neurotransmitter AAs – Glycine, glutamate, taurine, aspartate • Neurotransmitter proteins – Acetylcholine • Important to muscle contraction • Synthesis: – Acetyl-CoA and Choline » Choline acetyl transferase • Degradation – Acetylcholinesterase Amino acids • Catecholamines – Epinephrine, Norepinephrine • Synthesis – Tyrosine • All the products of this pathway have biological effects • L-DOPA – Used to treat Parkinson’s disease – Precursor to dopamine, nor-epi and epi – Precursor to melanin • Dopamine – Neurotransmitter – Sympathetic nervous system stimulant Amino acids • 5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) – Neurotransmitter – Synthesized from tryptophan – Contributes to well-being – Leads to melatonin • Produced in pineal gland • Important to circadian rhythms • Powerful antioxidant Regulatory peptides and proteins • Metabolic regulators – Insulin • Produced in beta cells (islets of Langerhans) of pancreas • Primarily Anabolic – Glycogen storage – Reduced lipid mobilization – Stimulates protein synthesis – Glucagon • Produced in alpha cells • Primarily “Anti-insulin” – Controlled • Basically by the blood glucose concentration • Somatostatin – Formed in delta cells – Prevents excessive insulin release following a meal Growth factors, gut and brain peptides • Somatomedins – IGF-1 and 2 • • • Gut peptides – Gastrin • • – – Increases GI motility Synthesized in gut, pancreas and hypothalamus Bombesin (Gastrin releasing peptide) • • – Stimulates bile release in response to fat in small intestine Synthesized in I cells of small intestine VIP • • – Stimulates secretion of HCl Released from G cells in stomach, pancreas and duodenum CCK • • Stimulates gastrin release Released from terminals of Vagus nerve Secretin • • • Cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis Produced in Liver Increase water and bicarbonate secretion into the small intestine Produced by S cells of duodenum Brain peptides – Endorphins • • Endogenous morphine Produced in brain, released via hypothalamus and pituitary