* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Translation - Crestwood Local Schools
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
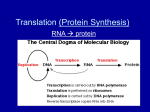
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Do these people represent DNA or RNA? How do you know? DNA • DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases • These Genes code for polypeptides (proteins) • Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells Genes & Proteins Proteins are made of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds 20 different amino acids exist Amino Acid Structure Polypeptides • Amino acid chains are called polypeptides Pathway to Making a Protein DNA mRNA tRNA (ribosomes) Protein Protein Synthesis The production or synthesis of polypeptide chains (proteins) Two phases: Transcription Translation mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus of eukaryotic cells The Genetic Code • A codon designates an amino acid • An amino acid may have more than one codon • There are 20 amino acids, but 64 possible codons • Some codons tell the ribosome to stop translating Codons • Sets of 3 Base Pairs • Each codes for an amino acid • Redundancy • Start codon AUG Codons • Sets of 3 Base Pairs • Each codes for an amino acid • Redundancy • Start codon AUG Name the Amino Acids • • • • • GGG? UCA? CAU? GCA? AAA? What does it mean to translate? To change from one form into another Big Picture overview of transcription and translation: Transcription: Making an RNA copy of the DNA Translation: Making a protein from the RNA copy How do we refine the central dogma to include transcription and translation? Why not just use the DNA to make a protein? So what is the biological understanding of TRANSLATION? the process of matching amino acids to corresponding sets of three bases (codons) and linking them into a protein. What are codons? AUGCCGUUAUUA Each series of corresponding three bases What are amino acids? 20 different small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. Often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins. How does TRANSLATION work? 1. You have a your resulting RNA strand from transcription UGACUUGGACUA 2. Each codon is translated into a specific AMINO ACID a. The tRNA reads the code on the mRNA and brings the right amino acid b. The ribosome links the amino acids into a chain to make a protein . Three Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized Messenger RNA (mRNA) • Long chain of nucleotides that carries the information for a specific protein • Made in the Nucleus (500 – 1000 nucleotides long) • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U ( no T ) • Copies DNA & leaves through nuclear pores Transfer RNA (tRNA) • Clover-leaf shape • Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid • Single stranded molecule with attachment site at one end for an amino acid • Opposite end has three nucleotide bases called the anticodon – Anticodon: three tRNA nucleotides that will hydrogen bond with the mRNA codon Codons and Anticodons • The 3 bases of an anticodon are complementary to the 3 bases of a codon • Example: – Codon ACU – Anticodon UGA U G A A C U Transfer RNA amino acid attachment site U A C anticodon Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • rRNA is a single strand 100 to 3000 nucleotides long • Globular in shape • Made inside the nucleus of a cell • Associates with proteins to form ribosomes • Site of protein Synthesis Ribosomes • Made of a large and small subunit • Composed of rRNA (40%) and proteins (60%) • Have two sites for tRNA attachment: – P and A Amino acid •Messenger RNA •Carries the message from the DNA to the ribosome to build a protein •Transfer RNA Ribosome •Transfers amino acids onto the protein as it is being made Transfer RNA (tRNA) •Ribosomal RNA •Part of the ribosome Codon Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Messenger RNA (mRNA) Translation • Translation is the process of decoding the mRNA into a polypeptide chain • Ribosomes read mRNA three bases or 1 codon at a time and construct the proteins Key things to remember • A protein always begins with the same START codon: RNA codon AUG and the amino acid methionine (met). • A protein is finished when it reaches a STOP codon: RNA codons: UAA, UGA, UAG • Don’t try to memorize the code. It will be given to you. Just learn the start codon. Site of Translation: Ribosomes Large subunit P Site A Site mRNA A U G Small subunit C U A C U U C G Step 1- Initiation • mRNA transcript start codon AUG attaches to the small ribosomal subunit • Small subunit attaches to large ribosomal subunit mRNA transcript Initiation aa1 aa2 2-tRNA 1-tRNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon G A U C U A C U U C G A mRNA Step 2 - Elongation • As ribosome moves, two tRNA with their amino acids move into site A and P of the ribosome • Peptide bonds link the amino acids together Elongation peptide bond aa1 1-tRNA anticodon hydrogen bonds U A C A U G codon aa2 2-tRNA G A U C U A C U U C G A mRNA aa1 peptide bond aa3 aa2 1-tRNA 3-tRNA U A C (leaves) 2-tRNA A U G G A A G A U C U A C U U C G A mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon aa1 peptide bonds aa2 2-tRNA A U G aa3 3-tRNA G A U G A A C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA aa1 peptide bonds aa4 aa2 aa3 2-tRNA 4-tRNA G A U (leaves) 3-tRNA A U G G C U G A A C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon aa1 peptide bonds aa2 aa3 3-tRNA aa4 4-tRNA G A A G C U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA peptide bonds aa1 aa5 aa2 aa3 aa4 5-tRNA U G A 3-tRNA G A A 4-tRNA G C U G C U A C U U C G A A C U mRNA Ribosomes move over one codon aa4 aa5 Termination aa199 aa3 primary structure aa2 of a protein aa200 aa1 200-tRNA A C U mRNA terminator or stop codon C A U G U U U A G 37 End Product –The Protein! • The end products of protein synthesis is a primary structure of a protein • A sequence of amino acid bonded together by peptide bonds aa2 aa3 aa4 aa5 aa199 38 aa1 aa200 NUCLEUS 1. mRNA is transcribed in the nucleus. mRNA Phenylalanine Methionine tRNA Lysine 2. mRNA enters cytoplasm & attaches to ribosome at the “start codon.” 3. tRNA with the correct anticodon brings in the next amino acid in the sequence. RIBOSOME Start codon mRNA RIBOSOME Growing polypeptide chain tRNA 4. The ribosome joins the two amino acids & releases the tRNA. Lysine tRNA 5. The ribosome moves along the mRNA to bind new tRNA molecules and amino acids. mRNA 6. The process continues until the ribosome reaches a stop codon. RIBOSOME Direction of translation Key things to remember • A protein always begins with the same START codon: RNA codon AUG and the amino acid methionine (met). • A protein is finished when it reaches a STOP codon: RNA codons: UAA, UGA, UAG • Don’t try to memorize the code. It will be given to you. Just learn the start codon. Practice Replication DNA Strand: ACTACGTTAGAACT Complimentary Strand? TGATGCAATCTTGA Practice Transcription DNA: ACTACGTTAGAACT mRNA: UGAUGCAAUCUUGA Practice (use your amino acid decoder) Translation mRNA: UGA U GCAAUCUUGA Amino acid sequence: met – gln – ser - STOP