* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Test 1 Review Three domains: Archae
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
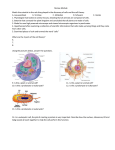
Biology Test 1 Review Archae- no nucleus, cells wall without peptidoglycan Bacteria- no nucleus, cells wall with peptidoglycan Eukarya- have a nucleus- Eukaryote Archaebacteria- “extreme bacteria” Cell Type- Prokaryote (no nucleus) Organization- Unicellular Cell wall- lacks PEPTIDOGLYCAN Nutrition- Heterotroph/ Autotroph (chemosynthetic) Eubacteria- “true bacteria” Cell Type- Prokaryote (no nucleus) Organization- Unicellular Cell wall- has PEPTIDOGLYCAN Locomotion: Squirm, flagella, cilia Nutrition- Heterotroph/ Authotroph (photosynthetic) Locomotion: Squirm, flagella, cilia ProtistaCell Type- Eukaryote (has a nucleus) Organization- Unicellular, Multicellular (colony) Cell wall- some yes, some no Nutrition: photosynthetic (autotrophic), or heterotrophic (eats) Locomotion: Yes (Cilia, Flagella, Ooze) Fungi Cell Type- Eukaryote Unicellular (yeast), Multicellular (molds, mushrooms) Cell Wall- Yes (Chitin) Nutrition- heterotroph (saprophyte/decomposer) Locomotion- No Plantae Cell type- Eukaryote Organization- Multicellular Cell Wall = Cellulose AnimaliaCell type- Eukaryote Organization- Multicellular (Specialized) Cell Wall- No Nutrition- Heterotroph (ingestion) Locomotion- Yes NutritionAutotroph (Photosynthetic) Locomotion- No Prokaryote Three domains: Biology Test 1 Review Characteristics of life 1.All living things are made of cells 2.All living things use energy 3.All Living things respond to stimuli- shiver when cold, change fur color, plants bend toward light 4.All Living things Reproduce- Sexual or asexual 5.All living things grow and Develop 6.All Living things Change to Fit Their Environment 7.All Living things have DNA 8.All Living things maintain a Stable Internal Environment- This is called HOMEOSTASIS Water – The O and H are held together by a Polar Covalent Bond Water is a polar molecule- which means it has a partial positive and a partial negative side The Oxygen has a partial negative charge because it has more positive protons to attract the negative electrons The Hydrogen has a partial positive charge It is able to dissolve many solutes because of its polarity It is called the Universal Solvent Water Molecule are attracted to the other end charge of other water molecules and are held together by Hydrogen Bonds Its polarity also allows for many of the properties that make water special: -Its frozen state is less dense than its liquid state Biology Test 1 Review Adhesion- is the tendency of water to stick to its container, this is part of what is responsible for plants being able to move water from their roots to their shoots. Also responsible for meniscus. -Cohesion- is the tendency of water molecules to stick together and is also part of what is responsible for moving water in plants -Surface Tension- is especially strong cohesion in the top layer of water molecules. Macromolecules Biology Test 1 Review Four Types of Macromolecules Function Dietary Energy; storage; Plant Structure Information Storage; Genetic Material Enzyme, Structure, Storage, Transport (Cell Membrane) Long term energy storage; Cell membrane; hormones (Steroids) Cell Membrane The Cell membrane is a Fluid Mosaic made up of a phospholipid bilayer and Proteins The Phospholipid Bilayer is made up of two layers of phospholipids with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail The hydrophobic tails face inward and the hydrophilic heads face outward This makes the Cell Membrane Selectively Permeable -It allows small, uncharged molecules through with the concentration gradient – Passive Transport -While keeping out large, charged particles Biology Test 1 Review Larger, Charged Particles require ENERGY to get through the Cell Membrane – Active Transport Active Transport uses ATP as its energy source Proteins are used to move some molecules Diffusion is the movement of molecules with the concentration gradient – from high concentration to low concentration Osmosis- Diffusion of water from where there is more water (low solute) to where there is less water (high solute) Hypotonic solutions have a less solute outside the cell than inside. This causes water to move in to equalize the concentration Isotonic Solution have the same amount of solute inside and outside Hypertonic solutions have more solute outside the cell then inside. This causes water to move out of the cell to equalize the concentration Endocytosis- Part of the cell membrane surrounds materials in a vesicle and carries them into the cell to be released inside. Used for: - Molecules that are too large to - Engulfing food- Requires the move through the cell use of ATP energy membrane - Active Transport Exocytosis: Part of the cell membrane surrounds materials in a vesicle and carries them out of the cell to be released outside. Used for: -Molecules that are too large to -Requires the use of ATP move through the cell membrane energy -Removing waste and worn out -Active Transport organelles