* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reorientation (AMA-1)
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
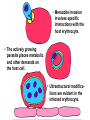
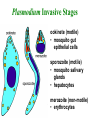
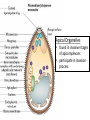
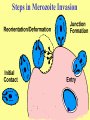
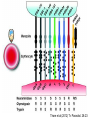
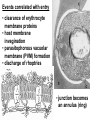
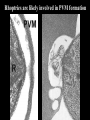
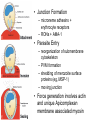
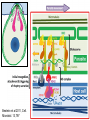
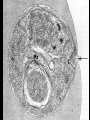
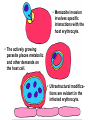
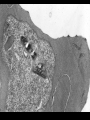
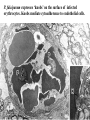
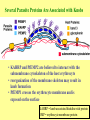
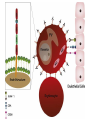
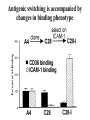
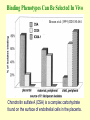
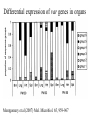
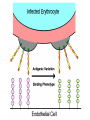
Cell Biology of Plasmodium Mark F. Wiser http://www.tulane.edu/~wiser/malaria/ • Merozoite invasion involves specific interactions with the host erythrocyte. • The actively growing parasite places metabolic and other demands on the host cell. • Ultrastructural modifications are evident in the infected erythrocyte. Plasmodium Invasive Stages ookinete (motile) • mosquito gut epithelial cells sporozoite (motile) • mosquito salivary glands • hepatocytes merozoite (non-motile) • erythrocytes Apical Organelles • found in invasive stages of apicomplexans • participate in invasion process Steps in Merozoite Invasion Reorientation • accompanied by erythrocyte deformation • AMA-1 implicated* • apical membrane antigen-1 • binds erythrocytes • antibodies inhibit invasion and reorientation • antibodies do not inhibit initial attachment *Apical Membrane Antigen-1 Mitchell et al (2004) Inf. Imm. 72, 154. Secretory (Apical) Organelles Organelle Shape Rhoptry Microneme Dense Granule Teardrop Ellipsoidal Spherical Size (nm) 300 x 600 40 x 100 120 - 140 Adhesins Localized to Micronemes •Merozoite proteins: • EBA-175 (sialic binding protein of P. falciparum) • Duffy-binding protein (P. vivax and P. knowlesi) •TRAP family*: • SSP2 (sporozoite surface protein-2) TRAP (thrombospondin-related adhesive protein) • Toxoplasma, Eimeria and Cryptosporidium proteins with homology to SSP2/TRAP • CTRP, circumsporozoite- and TRAP-related protein (Plasmodium ookinete stage) *Thrombospondin family characterized by von Willebrand factor type A domain. Functions in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. Invasion Receptors/Ligands Species P. falciparum P. vivax, P. knowlesi Host Receptor Merozoite Ligand glycophorins (sialic acid) EBA-175 Duffy Ag DBP Tham et al (2012) Tr. Parasitol. 28:23 • microneme secretion • receptor-ligand interactions • junction formation Electron micrograph from Aikawa et al (1978) J. Cell Biol. 77:72 Events correlated with entry • clearance of erythrocyte membrane proteins • host membrane invagination • parasitophorous vacuolar membrane (PVM) formation • discharge of rhoptries • junction becomes an annulus (ring) Rhoptries also participate in junction formation • Rhoptry neck proteins (RONs) inserted into host membrane • RON2 interacts with AMA-1 • Forms part of the moving junction • Highly conserved in Apicomplexa Tonkin et al 2011, Science 233,463 Rhoptries are likely involved in PVM formation • Junction Formation – microneme adhesins + erythrocyte receptors – RONs + AMA-1 • Parasite Entry – reorganization of submembrane cytoskeleton – PVM formation – shedding of merozoite surface proteins (eg, MSP-1) – moving junction • Force generation involves actin and unique Apicomplexan membrane associated myosin • TRAP necessary for invasion and gliding motility • actin-myosin motor = glideosome Besteiro et al 2011, Cell. Microbiol. 13,797 Merozoite invasion: a complex and ordered process • Initial Binding • merozoite surface proteins (eg. MSP-1) • Reorientation (AMA-1) • Microneme Discharge and Junction Formation • receptor-ligand interactions (adhesive proteins) • Rhoptry Discharge and Vacuole Formation • clearing of host membrane proteins • moving junction formation (RONs/AMA-1) • Parasite Entry • mediated by actin-myosin ‘glideosome’ • shedding of merozoite surface • Closure of PVM and Erythrocyte Membrane • Merozoite invasion involves specific interactions with the host erythrocyte. • The actively growing parasite places metabolic and other demands on the host cell. • Ultrastructural modifications are evident in the infected erythrocyte. Erythrocyte Modifications Affecting Permeability • In 48 hours parasite produces 20-30 merozoites • uptake of anions, sugars, amino acids, organic cations • New permeability pathways induced in host erythrocyte • Parasite modifies host cell by exporting proteins into host erythrocyte P. falciparum expresses ‘knobs’ on the surface of infected erythrocytes. Knobs mediate cytoadherence to endothelial cells. Several Parasite Proteins Are Associated with Knobs • KAHRP and PfEMP2 are believed to interact with the submembrane cytoskeleton of the host erythrocyte • reorganization of the membrane skeleton may result in knob formation • PfEMP1 crosses the erythrocyte membrane and is exposed on the surface KAHRP = knob associated histidine rich protein EMP = erythrocyte membrane protein PfEMP-1 Structure • family of ~60 var genes • mitotic recombinations continuously produce new variants • conserved intracellular C-terminus • acidic terminal segment (ATS) • binds cytoskeleton + KAHRP • transmembrane domain • variable extracellular domain composed of modules • 2-7 copies of Duffy-binding like (DBL) domains • 5 sequence types (a, b, g, d, e) • 0-2 cys-rich interdomain (CIDR) regions • participates in cytoadherence Possible Host Receptors • CD36 • Ig super-family (eg, ICAM-1) • endothelial protein C receptor • chondroitin sulfate A • E-selectin • thrombospondin • hyaluronic acid • Rosetting Receptors • CR-1 • glycosaminoglycan • blood group A Binding Sites Domain Receptor CIDR DBLa DBLb DBLg CD36 rosetting ICAM-1 CSA A high rate of antigenic variation is observed on the erythrocyte surface Roberts et al (1992) Nature 357:689 • agglutinating anti-sera used to define antigenic types • antigenic variants obtained from a cloned parasite line A switch rate of 2% per generation in absence of immune pressure. • clones also exhibited different ICAM1/CD36 binding phenotypes Antigenic switching is accompanied by changes in binding phenotype Binding Phenotypes Can Be Selected In Vivo Beeson et al (1999) JID 180:464 Chondroitin sulfate A (CSA) is a complex carbohydrate found on the surface of endothelial cells in the placenta. A Specific PfEMP1 Variant Binds to CSA • • • • VAR2CSA binds to CSA Found in most parasite strains Member of domain cassette (DC) 2 (defined combination of domains always found together) Members of DC8 and DC13 associated with binding to brain endothelial cells and severe malaria Claessens et al (2012) PNAS 109:E1772 Differential expression of var genes in organs Montgomery et al (2007) Mol. Microbiol. 65, 959-967 Expression of Particular var Genes May Correlate with Disease Manifestations and Virulence Var Gene Expression • one var gene is expressed at a time (allelic exclusion) • specific expression site in nucleus • repressor proteins bind promoters of nonexpressed variants • switching mechanism? Borst and Genest (2006) Nature 439, 926 SUMMARY • parasite modifies host via exported proteins – permeability changes – knobs + PfEMP-1 • PfEMP-1 participates in cytoadherence • immune evasion accomplished through antigenic switching (var gene family) • some var genes may correlate with specific disease manifestations and virulence • maintain chronic infections