* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Malaria based proteomics of erythrocyte surface proteins
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
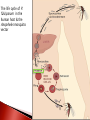
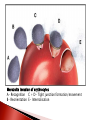
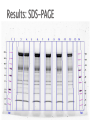
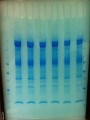
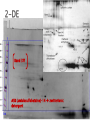
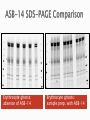
Kim Baron University of Pretoria, Department of Pharmacology Supervisor: Dr Duncan Cromarty Co-supervisor: Dr Stoyan Stoychev Few diseases have had same global health & economic impacts of malaria 300 million people affected globally each year & 0.7-2.7 million annual deaths Caused by protozoan parasite Plasmodium (falciparum) most severe form humans Discovered 100 years ago stage specific differential protein expression Control of malaria uses several approaches ◦ Improve diagnosis ◦ Improve prophylactic chemotherapy ◦ Integrated vector control Prevalence malaria evident worldwide ◦ Drug-resistant parasites ◦ Insecticide-resistant vectors New malaria drugs are expensive & limited in supply Safe, effective & affordable treatment critical global public health priority The life cycle of P. falciparum in the human host & the Anopheles mosquito vector Merozoite invasion of erythrocytes A- Recognition C + D- Tight junction formation/movement B- Reorientation E- Internalisation Merozoite invasion of RBC’s is highly complex cascade of specific molecular interactions Complete receptor-ligand interactions unknown Invasion is central & essential in development of malaria speed & efficiency contributed to evolutionary success & parasitemia Inhibition of parasite invasion before manifestation of clinical symptoms Advantage To identify which erythrocyte surface proteins act as receptors during the initial recognition and binding of the Plasmodium falciparum merozoite to the erythrocyte during the invasion process of the malaria parasite Culturing and synchronisation of 3D7 Plasmodium falciparum parasites RBC ghost sample preparation Protein fingerprinting of RBC ghost proteins SDS-PAGE Protein fingerprinting of RBC ghost proteins 2-DE Merozoite treatment phospholipase C to cleave GPI anchors Free merozoite surface proteins incubated with RBC’s & cross-linked Protein fingerprinting of merozoite-bound RBC ghosts 2DE Comparison: free RBC ghosts/merozoite-bound RBC ghosts/Free merozoites Isolate spots of interest PMF RBC membrane proteins involved in P.f invasion by LC-MS/MS Band 3?? ASB (amidosulfobetaine)-14 zwitterionic detergent * Erythrocyte ghosts: absence of ASB-14 * Erythrocyte ghosts: sample prep. with ASB-14 ASB-14 utilisation with adjusted voltage settings Active sample loading 10% T gel instead of 4-20% T Plasmodium falciparum complex & “intelligent” RBC’s are abundant & fragile Avoids damaging RBC Protected from immune system To potentially stop deadly parasite new innovative therapies Determining exact R-L during invasion discovery of new key targets for drug & vaccine based antimalarial strategies