* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion Lab Make
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
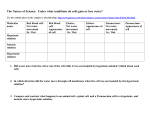
Name: _____________________________________ Per: ____ TOC#____ Diffusion Lab Make-up Introduction: Diffusion is the process in which substances move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. This is particularly important in regulating a cells equilibrium. Diffusion allows substances such as nutrients, water, oxygen, and cellular wastes are transported between living cells and their environment. This activity will help you explore the relationship between diffusion and cell size by experimenting with model “cells.” In this experiment, you will use agar cubes to which the indicator bromthymol blue has been added. Bromthymol blue is an acid/base indicator that turns yellow in the presence of an acid such as vinegar. Thus the surface of the agar cubes will turn yellow immediately when put into a vinegar solution. The agar cubes are semi-permeable like a cell membrane and the vinegar will diffuse through the cube and gradually turn the inside of the cube yellow. The guiding question for this lab is: What determines the efficiency of diffusion throughout the model “cells”? Does size matter? Will the smaller cells or the larger cells be yellower in the middle? Focus Questions: By the end of this lab, you should be able to answer the following questions. ● What is diffusion? ● How does cell size relate to diffusion? Pre-Lab Questions: In order to be completing this lab, first, answer the following questions. 1. Define Diffusion 2. Define osmosis 3. Define hypotonic, hypertonic, isotonic 4. Define Passive transport 5. Define Active transport 6. What is the cell membrane made of? Watch the video: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_diffusion_works.html After the video scroll down and take the quiz. Submit your answers. When you have the results of your quiz, write down your score here: ________ Name: _____________________________________ Per: ____ Watch the video: TOC#____ http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_osmosis_works.html After the video scroll down and take the quiz. Submit your answers. When you have the results of your quiz, write down your score here:___________ Visit: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Directions: Complete the graph and answer the following questions while completing the virtual lab. Data Table: Concentration of Solution vs. Type of Cell Red Blood Cell: Net water movement in/out Red Blood Cell: Appearance of Cell Elodea: Net water movement in/out Elodea: Appearance of Cell Paramecium: Net water movement in/out Paramecium: Appearance of Cell Hypotonic Solution Isotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Analysis Questions: 1. Did water move into or out of the cell when in a hypotonic solution? What about in a hypertonic solution? 2. Could elodea or paramecium from a freshwater lake be expected to survive if put into the ocean? Explain. 3. Explain why a salad becomes soggy and wilted when left with dressing on it? Explain why, in terms of osmosis.