* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Cell Test
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
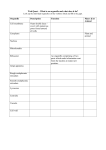
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Biology Cell Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1, Who. wasone of the first people to-identify and seecorkeells? -,a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek c. Matthias Schleiden h. Robert Hooke d. .Rudojf Virchow 2. The a. b. c. d. ; -...'... work of Schleiden and Schwann can be summarized by saying that all plants are made of cells. all animals are made of cells. plants and animals have specialized cells. all plants and animals are made of cells. 3. Which of the following is NOT a principle of the cell theory? a. Cells are the basic units of life. b. All living things are made of cells. c. Very few cells reproduce. d. All cells are produced by existing cells. 4. The cell theory applies to a. bacteria. b. plants and animals. c. d. multicellular organisms. all of the above 5. Looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokaryote. How do you know? a. The cell lacks cytoplasm. c. The cell lacks a nucleus. b. The cell lacks a cell membrane. d. The cell lacks genetic material. 6. Eukaryotes usually contain a. a nucleus. b. specialized organelles. c. d. genetic material. ail of the above 7. Which of the following orgamsms are prokaryotes? a. plants c. bacteria b. animals d. all of the above 8. Which of the following is NOT found in the nucleus? a. cytoplasm c. chromatin b. nucleolus d. DNA 9. Which organelle breaks down food into molecules the cell can use? a. Golgi apparatus c. endoplasmic reticulum b. lysosome d. mitochondrion 10. Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus c. vacuole b. mitochondrion d. ribosome . . ,- Name: . ID: A 11. Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use? . . .. a. chloroplast ' ' c. endoplasmic reticulum • b. Gplgi apparatus d. mitochondrion 12. Which organelles help provide cells with energy? >: a.•- mitochondria and chloroplasts • c;' b. rough endoplasmic reticulum d. ____ smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus and ribosomes 13. Which organelle would you expect to find in plant cells but not animal cells? a. mitochondrion c, chloroplast b. ribosome d. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 14. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape c. surrounds the cell b. contains DNA d. helps make proteins 15. Which structures carry out cell movement? a. cytoplasm and ribosomes b. nucleotus and nucleus c. d. microtubules and micro filaments chromosomes 16. The main function of the cell wall is to a. support and protect the cell. b. store DNA. c. d. direct the activities of the cell. help the cell move. 17. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is a. found in all organisms. b. composed of a lipid bilayer. c. d. a flexible barrier. usually made of tough fibers. 18. Which of the following is a function of the cell membrane? a. breaks down Mpids, carbohydrates, and proteins from foods b. stores water, salt, proteins, and carbohydrates c. keeps the cell wall in place d. regulates which materials enter and leave the cell Name: ID: A •'•-..-" - " Figure 7-3- Nucleus 19. In Figure 7-3, the structure labeled "D" is the ' - ' A- Nucleus B- Nuclear Envelope • C- Nuclear Pore D- Nucleolus 20. Using Figure 7-3, Which letter represents the part of the nucleus that makes nbosomes? A- Letter A B- Letter B C- Letter C D- Letter D 21. The image in Figure 7-3 is a nucleus, the letter C is called the A- Nucleus B- Nuclear Envelop C- Nuclear Pore . D- Nucleolus D N II Figure 7—5 22. Interpreting Graphics Which drawing in Figure 7-5, -I or II- is a plant Cell? A-1 B- II 23. Using Figure 7-5, in which cell would a pair of centrioles be found? A-1 B- II ID: A Name: p-^-^-^^ A plant cell 24. Figure 7-6 Using Figure 7-6, what letter indicates the organelle responsible for photosynthesis? A-Letter D B-Letter F C-Letter H D-Letter! 25. Using Figure 7-6, which letter indicates the vacuole? A- Letter C B- Letter D C- Letter F D- Letter H 26. Using Figure 7-6, choose the letters that represent organelles that are found only in plant cells, not in both plant and animal cells. A- Letters C and D B- Letters F and J C- Letters D and H D- Letters C and J Name: ID: A Matching ' •. ..' ' ; ... - •., ••"-. •> • AL -;- -- f. • • ' • . .-.. <2? Using the Microscope Above Match the part of the microscope with the Diagram 27. Coarse Adjustment 28. Objectives 29. Diaphragm 30. Arm 31. Fine Adjustment 32. Light Source 33. Stage 34. Eyepiece Match the part of the microscope with its function d. Coarse adjustment Eyepiece e. fine adjustment Stage c. Objectives 35. Focuses image on low power 36. View image, has a magnification of 37. Holds the slide 38. Focuses image on medium and high power 39. Low, Medium and High power magnification - Name: ID: A Macromolecule Carbohydrates Monomer "~A \ None Ami-no Acid -B Elements C,H,Oin 1:2:1 C, H, O E ' - \c Acid nucleotlde 40. Store and transmit genetic information 41. Protein 42. Monosaccharide 43. Only macromolecule to contain Sulfur (S) 44. Lipids 45. Cholesterol 46. DNA, RNA C,H,0,N,P Function Provide energy for Sugar, starch . the cell Store Energy C \ Structure to build Enzymes, muscle, beans, cell parts, biological catalyst, "meat defense, Communication, AB \s AC \e the Tabl