* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer Key: What do I need to know for the test
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
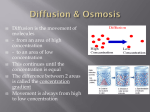
Answer Key: What do I need to know for the test? 1. The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and proteins. Phospholipid-the polar head loves water (hydrophilic) and the lipid tail hates water (hydrophobic) 2. The three proteins found in the cell membrane are a. receptor b. channel c. marker 3. Function (jobs) of the proteins: a. receptor- send messages or signals b. channel- move materials in and out of cell c. marker- I.D. tag , identify the cell 4. Diffusion is the movement of materials (ions, molecules, gases) from an area of high conc. to low conc. Some examples of diffusion are: burning toast, perfume sprayed, food coloring added to water, baggie experiment (starch and iodine) Note: Most materials can diffuse under the right circumstances. 5. Osmosis is the movement of water across a cell membrane from an area of high conc. to an area of low conc. Osmosis only occurs with water. 6. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of materials in or out of the cell through channels in the membrane from an area of high conc. to an area of low conc. Facilitated diffusion requires channels. 7. Diffusion, osmosis and facilitated diffusion all move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. NONE OF THESE PROCESSES REQUIRES ENERGY! 8. Passive transport does not require energy. It is the movement of materials from area of high conc. to low conc. 9. Active transport is the movement of materials from an area of low conc. to an area of high concentration. Active transport requires energy. 10. Endocytosis is the movement of large materials into the cell. Needs energy. Exocytosis is the movement of materials out of the cell. Needs energy. Some materials that need to get out of the cell are: wastes and hormones 11. Two types of endocytosis are: pinocytosis and phagocytosis Pinocytosis is when the cell “drinks” liquids with dissolved materials in it. Phagocytosis is when the cell “eats” solid particles. 12. Active transport moves the materials from low concentration to high concentration. Forces it against the concentration gradient. 13. Isotonic solution is a solution that has the same amount of dissolved materials and water that is found inside the cell. They are equal. 14. Hypotonic solution has more water and less dissolved materials than inside the cell. So water will flow into the cell. Cell swells. Some cells can protect themselves from bursting by: Cell wall Contractile vacuole Cells are surrounded in the same solution as the solution inside the cell (example: human cells and plasma) 15. Hypertonic solution has more dissolved materials and less water so the water will flow out of the cell and into the solution. Cell will shrink. Becomes dehydrated 16. Selectively permeable means that only some materials can enter of leave. Permeable means that anything can enter of leave. 17. Molecules will diffuse whenever there is a concentration difference, this will continue until equilibrium is reached.