* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 5.2 - Cells: The Basic Unit of Life ANIMAL CELL
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
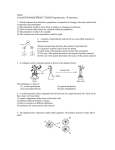
Reproduction.notebook May 01, 2012 Section 5.2 - Cells: The Basic Unit of Life ANIMAL CELL Cell Membrane - entire cell is covered with the cell membrane. - acts like a gatekeeper, controlling the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Nucleus - acts as the control centre, directing all of the cell's activities. - genetic information is organized into threadlike structures called chromosomes - each chromosome contains many different genes. - genes are units of genetic information that determine the specific characteristics of an individual. Cytoplasm - area of the cell where the work is done. - nutrients are absorbed, transported, and processed within the cytoplasm. - contains a number of different organelles that each have a specific form and function - an organelle is a specialized structure inside the cell. Reproduction.notebook May 01, 2012 Chromosomes are thread-like structures that carry genetic information. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of every cell. Genes are units of genetic information that determine the specific characteristics of an individual. The nucleolus is the darker area found inside the nucleus. Ribosomes build proteins that are necessary for cell growth and reproduction. Reproduction.notebook The endoplasmic reticulum is a series of canals that transports materials to different parts of the cell. Mitochondria provides the cell with energy. Centriole is a small protein structure critical for cell division. Vacuoles are fluid-filled storehouses that contain water, food, wastes and other materials. May 01, 2012 Reproduction.notebook May 01, 2012 Golgi bodies store proteins until they are needed by the cell. Lysosomes are saclike structures that contain proteins that break down food and digest wastes and worn-out cell parts. Comparison of Plant and Animal Cells Reproduction.notebook May 01, 2012 Plant cells contain all the organelles found in animal cells plus a few other structures. Cell Wall - surrounds the cell membrane. - composed of rigid material called cellulose. - protect and support plant cells. Chloroplasts - organelle containing chlorophyll used in photosynthesis. Vacuoles - both animal and plant cells contain vacuoles, but in plant cells the vacuole is much LARGER. Reproduction.notebook Cell Parts Assignment Pages 142 & 143 May 01, 2012 Attachments Parts of cell webquest.docx DNA fingerprint questions.docx