* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 Gene Transfer in Bacteria Conjugation Hfr Cells
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
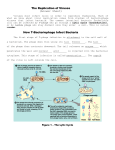
Gene Transfer in Bacteria • Conjugation – Bacterium to Bacterium gene transfer Chapter 8 • Transformation – Bacterium takes up naked DNA Bacterial and Viral Genetic Systems • Transduction – Bacterial virus carry DNA from one Bacterium to another Figure 8.9 Conjugation Bacterium to Bacterium (Lederberg and Tatum 1946) Hfr Cells • F Factor is integrated into the bacterial chromosome • Behave as F+ cells 1 Figure 8.14 Figure 8.15 Should say “different alleles” Mapping Through Interrupted Conjugation • Conjugation between Hfr and F- cells Mapping Bacterial Genes • Conjugation interrupted at selected intervals Conjugation Interuption • Time required for gene transfer indicates relative position Figure 8.17 2 Figure 8.18 Note the different orientations of the F Factor Different Hfr strains have different points of integration of the F Factor into the bacterial chromosome. Figure 8.18 3 Problem Set 4B • We can use interrupted conjugation data to map bacterial genes. Gene Transfer and Antibiotic Resistance Gene Transfer and Antibiotic Resistance • Continuous use of antibiotics selects for resistance • Antibiotic resistance genes located on R plasmids • Some carry resistance to multiple antibiotics • Can be transferred among bacterial species Transformation Transformation • Cells capable of taking up DNA are called Competent Uptake of Naked DNA • The DNA need not be bacterial. • Cells that receive genetic material through transformation are called Transformants 4 Figure 8.21 Mapping Genes Through Cotransformation • Observe the rate at which two or more genes are transferred together (cotransformed) • The rate of cotransformation is inversely proportional to the distances between genes. Problem Set 4B • We can use cotransformation data to map bacterial genes. Bacterial Genome Sequences • The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) The DOE JGI can sequence an entire bacterial genome (8X coverage) in a day…. …assuming they wanted to. – www.tigr.org – Comprehensive Microbial Resource • Contains: – 168 complete genomes (18 Archaea, 150 Bacteria) – 2 partial genomes 5 Viral Genetics A VIRUS is a simple replicating structure composed of nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat. T4 Bacteriophage Viral Genomes • DNA or RNA • Circular or Linear • Double or Single stranded Phage Life Cycle • Lytic cycle: – Phage attaches to receptor on the cell – Phage injects DNA into cell – Phage DNA is replicated, transcribed, and translated – New phage particles assembled, cell lyses. VIRULENT Phages reproduce strictly through the lytic cycle and always kill their host cells. 6 Phage Life Cycle Temperate Phage can use either the lytic or the lysogenic cycle • Lysogenic cycle: – Phage integrates into bacterial genome (PROPHAGE) – Prophage is replicated with bacterial genome and passed along to daughter cells when bacteria divide. – Stimuli cause prophage to dissociate from bacterial genome and enter the lytic cycle. Figure 8.23 A Plaque A lawn of bacterial cells Gene Mapping in Phages • Crosses between viruses with different genotypes • Recombinant progeny identified and counted • Example: Hershey and Rotman (1949), T2 bacteriophage Phage T2 Host Range Plaque Morphology • h+: infects Type B E. coli, not B/2 • r+: small plaques with fuzzy borders • h-: infects both types • r-: large abnormal plaques with distinct borders 7 Figure 8.25 Transduction Using Phage to Map BACTERIAL Genes Figure 8.26 Transduction • Generalized Transduction: – Any gene may be transferred • Specialized Transduction: – Only genes near particular sites on the bacterial chromosome are transferred 8 Figure 8.27 Figure 8.28: Mapping with transduction Specialized Transduction • Only genes near specific sites are transferred. • Requires lysogenic phage. • See Figure 8.29 (If you are interested) Complementation Test in Phage • Heterozygotes can have the mutations in TRANS (located on different chromosomes) or in CIS (located on the same chromosome). • If the mutations are in TRANS and are in the same locus (cistron): – No protein is produced (mutant phenotype) Figure 8.32 The problem set frustrates and and infuriates me! E.coli strain K Complementation A functional gene defined by the complementation test 9 Viral Genomes • First genome sequenced: ΦX174 – Overlapping genes! Figure 8.33 Figure 8.33 RNA Viruses • • • • Influenza Colds Polio Aids • Positive Strand RNA Viruses: genomic RNA codes directly for protein • Negative Strand RNA Viruses: complementary copy of genomic RNA codes for protein 10