* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria or How
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
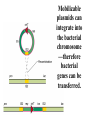
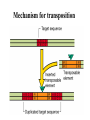
The exchange of Genetic Material between bacteria or How bacteria acquire resistance to antimicrobial agents in nature Modes of genetic exchange transformation phage mediated transduction conjugation transposition Transformation of bacteria with linear DNA—some cells are naturally competent for the uptake of DNA Plasmids are autonomously replicating circular DNA molecules that can be used to artificially transform bacteria— naturally competent cells can take up a plasmid, such plasmid does not need to integrate with the chromosome for maintenance!! Generalized transduction mediated by bacteriophages Conjugation —a mechanism by which mobilizable plasmids can be transferred from one bacterium to another Note tra genes, oriT and antibiotic resisitance genes Conjugation—a mechanism by which mobilizable plasmids can be transferred from one bacterium to another Note conjugation bridge formed between donor and recipient cells Mobilizable plasmids can integrate into the bacterial chromosome —therefore bacterial genes can be transferred. Transposons that carry antibiotic resistance genes can randomly “hop” into a bacterial chromosome Mechanism for transposition ABR ABR