* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and function of the cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
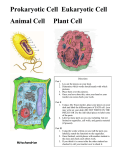
Smallest unit of life, Discovered by Robert Hooke 1695 Cell Theory: 1. All living things have cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of life and function 3. Cells only come from preexisting cells Variety of sizes and shapes Nerve cells shaped like fingers Most cells are round in shape Some cells change shape ◦ White blood cells The shape of a cell depends on the cell membrane and it’s function Cells are microscopic for the most part Some can be as large as 6ft in giant algae The cell size is limited by the ______________ of the cell membrane A cell can only grow so large then it will burst : structures in a cell that perform a specific function : these are cells with membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus : these are cells that do not have membrane-bound organelles or a nucleus It is : only certain things may pass through Forms a : 2 layers of lipids like a sandwich 1. Maintains the shape of the cell and 2.protects it Fats and proteins are embedded in the phosholipid bilayer : have two ends on them that keep water and nutrients inside Form a bond that is difficult to break These lipids are vital to the cell’s survival Acts like a floating layer, constantly changing shape Do 3 things: 1. Hold the membrane together 2. Allow for channels to be made in the membrane 3. Act as receptors for hormones and other compounds Model of the cell membrane that shows it’s “dynamic ability”, how it is more like a liquid than a solid The patterns of lipids and proteins are always changing Powerhouse of the cell Transfers energy from ATP to make the cell function Has it’s own DNA,most important organelle to the cell Muscle cells will have more mitochondria than other cells Most numerous organelle in a cell Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes They are not covered in a membrane They synthesize, or create, proteins Smallest of the organelles Vital to cell function and reproduction Found floating in the cytoplasm and on the rough ER ◦ Proteins made on free-floating ribosomes are used within the cell; proteins made on rough ER are usually shipped to the cell membrane or out of the cell Known as the ER, System of tubes and channels “highway” inside of the cell 2 types rough and smooth Rough ER has ribosomes along the outside of it Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is found in liver cells The amount of ER in a cell will fluctuate depending on how active a cell is in the body Makes proteins that are shipped to the cell membrane or out of the cell completely; the proteins made here are sent to the Golgi apparatus for packaging and export System of membranes within the cell used to package and ship proteins “UPS” of the cell Modifies or changes proteins before they leave the cell Allows cells to take proteins and ship them to other cells to be used Often located next to the ER Small spheres containing enzymes used for digestion Also eat up harmful bacteria and cells Not found in plant cells, only animal cells In humans, these organelles aid in development by destroying certain fetal tissues Houses the DNA in the cell Largest organelle in the cell Controls all of the functions of the cell Must divide when cells reproduce Has it’s own membrane around it Controls growth, metabolism and genetics of a cell Nucleolus: small part inside nucleus that makes ribosomes Found in plant cells Less flexible than cell membrane Gives plant cells the ability to stand up and grow into trees, flowers etc. Cell wall is thicker than cell membrane : Contain digestive enzymes in plants. Some plants will store toxins in the vacuoles that are poisonous, like poison ivy : contain chlorophyll so that plants can make food from sunlight Chlorophyll is usually a shade of green Long protein strands found in the cell Provide support for the cell Help to maintain the shape of a cell Help in the movement of chromosomes when the cell divides Vital to the survival of the cell, if these proteins die the cell will loose it’s shape and die as well Assist in movement of the cell : Hair-like extensions on the outside of the cell membrane : whip-like tail on the cell membrane of cells Sperm cells use flagella to swim towards the egg cell Cilia are found in lung cells to sweep out debris Similar cells that are grouped together form . 4 main types of tissues: muscle, nervous, connective and epithelial. Organs are a bunch of tissues that work together to perform a function. Example: the heart Many organs working together are an : digestive system uses the stomach, intestines, kidneys etc. Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Organ systems Organism