* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembling peptide wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
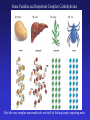
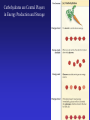
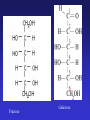
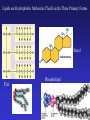
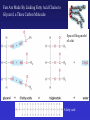
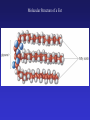
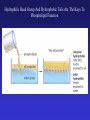
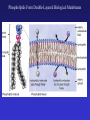
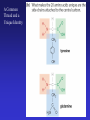
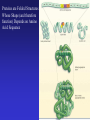
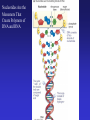
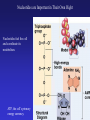
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. Never forget the axiom – structure dictates function. Some major types of biological molecules. Molecules of Life How do you build a cell? Start with water, add lots of small carbon-containing molecules and ……. use these four major classes of biological molecules. Monomers, Polymers and Macromolecules Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are used for energy and to create structures. The building blocks for carbohydrates are simple sugars. Three views of glucose, a common simple sugar. Linking Simple Sugars – the First Step to a Polymer monosaccharides a disaccharide A complex carbohydrate is a long-chain polymer made of simple sugars. Some Familiar and Important Complex Carbohydrates Note the way complex macromolecule are built by linking simple repeating units. Carbohydrates are Central Players in Energy Production and Storage Complex Carbohydrates Are Often Used to Create Structures Cellulose is the most abundant macromolecule on earth – and you’re probably wearing it now. Fructose Galactose Lipids are Hydrophobic Molecules That Exist In Three Primary Forms Sterol Fat Phospholipid Fats Are Made By Linking Fatty Acid Chains to Glycerol, a Three Carbon Molecule Space-filling model of a fat A fatty acid Molecular Structure of a Fat Fats are Used in Energy Storage and Production The Degree Of Saturation In A Fat Affects Its Physical And Health Properties Where are the double bonds? Phospholipids are Building Blocks of Cellular Membranes The hydrophilic head group and hydrophobic tails are the keys to phospholipid function. Phospholipids have a molecular Jekyll and Hyde split personality. Hydrophilic Head Group And Hydrophobic Tails Are The Keys To Phospholipid Function Phospholipids Form Double-Layered Biological Membranes Protein Proteins are THE key elements of life. Forget DNA, proteins rule. Remember the principle - structure determines function. Since proteins are the key players of the cell, it follows that protein structure determines cell function. Some of the Diverse Functions of Proteins Proteins are Linear Chains of Linked Amino Acids A Common Thread and a Unique Identity Amino Acids, Peptide Bonds, Polypeptides, Protein Proteins are linear chains of 20 different building blocks called amino acids. Peptide bonds Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds – a form of covalent bond. Proteins are Folded Structures Whose Shape (and therefore function) Depends on Amino Acid Sequence Nucleic Acids There are two kinds of nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. Both are involved in the storage and flow of information from gene to gene product. Recently, we’ve learned that RNA also plays important regulatory roles. DNA Nucleotides Are the Monomers That Create Polymers of DNA and RNA Nucleotides are Important in Their Own Right Nucleotides fuel the cell and coordinate its metabolism. ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency. Some Useful Nomenclature Learn to recognize these chemical groups.