* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 2.3 and 2.4 Guided Notes
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
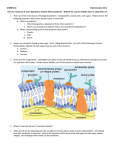
Name ______________________________ Class Period _______ The Molecules of Life: Chapter 2.3 - 2.4 Guided Notes - CP • • • • Organic Molecule - • Hydrocarbons - • Inorganic Molecules- Carbon is an essential element in organic molecules • One carbon atom can bond with up to ____________ other atoms Carbon-based (Organic) molecules have three general types of structures. • _____________________________________ • _____________________________________ • _____________________________________ Four main types of organic molecules are found in living things • • • • • • Monomers bonded together build polymers (Large molecules) • ____________________ Small chemical unit that makes up a polymer. (Individual building block) • ____________________ Molecules made of many monomers Building and Breaking Down Polymers • _______________________________________________ • Reaction that removes water from two molecules to bond them together (Creates a polymer) • Breaking Down a Polymer Chain • _______________________________________________ •Reaction where water is added to a molecule to break a bond. • Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are _____________________ made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen • In the ratio: ___C:___H:___O • Monomers = Simple sugar molecules called: ____________________________________________ • Polymers = Complex sugar molecules made of many monosaccharides called: _______________________________________________ Functions of Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are the ________________________________________________________________ • Other carbohydrates are used in cell structures. Type of Carbohydrate • Example • • • • • • Lipids • Elements are C,H,O • Monomers = ______________________ & ____________________ • • Main categories = ______________, ______________, ______________, & ______________ • Lipid Polymers - Triglyceride Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. • Saturated fatty acids • • Unsaturated fatty acids • • ___________________________________________________________________________ Lipids are Hydrophobic!! • • ___________________________________________________________________________ Hydrophobic = Functions of Lipids: 1. 2. 3. • Phospholipids • **Are the main part of all __________________________**_ • Phospholipid Structure • • • ___________________________________________ • ___________________________________________ Which part of a phospholipid avoids water and which part of a phospholipid attracts water? Explain why? • Proteins • Made of elements: • Monomer = • Polymer = • Amino Acids = ______________________________ • Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins!! • All amino acids have a carboxyl group and amino group. • • Amino Acids = Building blocks of Proteins • • Amino acids are different by _________________________________________________________ Amino acids are linked by _________________________________________ • A chain of amino acids is a protein. • Each protein has a unique _______________________!!!!!!! Functions of Proteins 1. 2. 3. 4. Proteins – Denaturation Structure is key to the function of enzymes. • If…… • The order of amino acids changes or • The temperature or pH changes to much Then….. • The protein will not function!! • _________________________________________________ when an unfavorable change in the temperature or pH cause a protein to unravel and lose its shape (this cannot be reversed) • Example: scrambled eggs are denatured protein • Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA) • Made of elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous • • Monomers = ________________________________________________ • Polymers = _________________________________________________ Nucleotides = Monomers • Nucleotide Structure: 1. 2. 3. • There are __________________ different nucleotides. • Only the structure ________________________________________________________________ • Nucleic Acids – Function 1. DNA - stores genetic information. 2. RNA - Carries message from DNA to create proteins! 3. Cellular energy molecule - ATP • Enzymes • Chemical Reaction Review: • Reactant + Reactant Products • Activation Energy: _______________________________________________________ • Cells can’t be heated so enzymes are needed to “start-up” chemical reactions in your body • _____________________________________– compounds that speeds up reactions by lowering activation energy • Speed up chemical reactions in your body! • Enzymes are ______________ _______________ !!!! • • Each enzyme is ___________________ and speeds up only one type of reaction. • (Like a LOCK and KEY) • Example: Amylase – only breaks down starches. Substrate Enzyme Complex Substrate Active Site