* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Four
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Counterproductive work behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
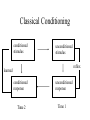
HRM 601 Organizational Behavior Session 4 Learning & Its Applications Learning • A relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience • Learning and performance -- Performance is an indirect measure of learning but is influenced by other factors such as motivation and fatigue Learning In Organizations • Formal learning – skill training – orientation – rules and regulations • Informal learning – norms – attitudes – shortcuts in doing your job CLASSICAL Classical Conditioning CONDITIONING conditioned stimulus unconditioned stimulus reflex learned conditioned response Time 2 unconditioned response Time 1 Some Basics • Extinction -- eliminating the response • Generalization -- extending the response to similar stimuli • Discrimination -- limiting the response to a specific stimulus • Higher order conditioning -- extending the response to remote conditioned stimuli Operant Conditioning ANTECEDENT A cue about consequences ex. advice BEHAVIOR CONSEQUENCE Desired organizational behavior ex. promptness Positive reinforcement ex. attention Negative reinforcement ex. anxiety Qualities Of Reinforcement • • • • Immediate Vs. delayed Contrived Vs natural Large Vs small Relative size Reinforcement Schedules • Interval schedules -- time based – fixed interval: ex. salary – variable interval: ex. spot inspections • Ratio schedules -- performance based – fixed ratio: ex. piece rate – variable ratio: ex. gambling on slot machines Shaping • Reinforcement of successive approximations of desired behavior • ex. shaping neatness by rewarding behaviors which gradually move towards keeping a workplace neat Traps & Fences • Traps -- behaviors with short term gain, long term pain – smoking, eating sweets, procrastination • Fences -- behaviors with short term lack of consequence or even mildly aversive consequence – flossing, getting right on the job, eating broccoli Punishment/Discipline • Defined -- the application of aversive or unpleasant consequences to a behavior. A punishment reduces the likelihood of a behavior occurring. • Like a negative reinforcer, it is unpleasant but a negative reinforcer strengthens and sustains behaviors. Punishment/Discipline weakens and eliminates behaviors. Problems In The Process • Is it truly punishment? • Is the timing delayed? • Is the punishment strong enough A Case Against Punishment • • • • It requires monitoring It is wasteful of supervisor’s time It only suppresses behavior It has undesirable side effects – fear, hostility, revenge • Nonetheless it is essential Effective Punishment/Discipline • • • • Apply Before the Behavior Takes Root Make It Quick and Strong Enough Punish the Act, Not the Person It Should Be Consistent Across Time and People • It Should Have Informational Value • It Is More Effective in a Warm and Supportive Relationship Observational Learning • Learning by watching • Distinctiveness of the theory – – – – – cognitive vicarious learning motivation active efficient Vicarious Learning • Modeling • Ability and practice • Vicarious reinforcement Motivation • Self-efficacy -- self-judgment concerning ability to perform an act. – positive enactment – modeling – coaching Self-control • Arrange work environment so that negative behaviors are reduced and positive ones increased. Engineer your antecedents (signals) for effective behavior • Self-reward -- use more preferred activities as a reward for accomplishing less preferred ones.