* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download introduction_to_micr..
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
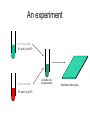
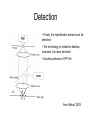
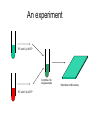
Introduction to Gene Expression Analysis Phillip Lord Resources http://www.ebi.ac.uk/microarray/biology_intro.html http://www.mged.org/ http://www.tigr.org/tdb/microarray/ Microarray Bioinformatics Dov Stekel Product Details: Paperback 280 pages (September 8, 2003) Publisher: Cambridge University Press Language: English ISBN: 052152587X How do we measure gene expression? • Oldest technique is to look at a phenotype. • In this case, the ura4+ gene from S.pombe • Most other techniques based on hybridisation. – Northern Blot – Quantative RT-PCR Microarray analysis • Whole genome sequencing makes it possible to predict the entire gene complement • Various technologies have built on this knowledge to produce systems that will monitor the expression (usually transcription) at the whole genome level – Measurement of global transcription is called transcriptomics • Come by a variety of names – gene chips, arrays, DNA arrays. Can be somewhat confusing what is actually being described. • Not to be confused with Genotyping Microarrays Generating Microarrays • There are many different systems for generating microarrays – spotting • original technology, now rather old • good for “one off” arrays – in-situ synthesis • newer, more reproducible • expensive first time around, then cheaper Spotting • Synthesize DNA, spot onto glass slides, fix. A Spotting Robot The head A Spotting Pin taken from Stekel, 2003 In-situ synthesis • • • • Uses chemically protected nucleotides Specific spots are “de-protected” Can then extend these oligos Different techniques for deprotection Masked Synthesis • Uses masks much like silicon chip production • Masks are expensive • Good for bulk production, standard arrays Photo deprotection • A light source is used to deprotect oligos • Essentially, this is much the same as an LCD projector. from Stekel, 2003 InkJet Synthesis • An InkJet head is used to place nucleotides at the appropriate place on the array An experiment RT with Cy3 dCTP Two Samples Combine into single sample RT with Cy5 dCTP Hybridise to Microarray Hybridisation from Stekel, 2003 Detection • Finally, the hybridisation extract must be detected • The technology is related to desktop scanners, but more sensitive. • Usually produces a TIFF file from Stekel, 2003 The end result from Stekel, 2003 Problems • We are looking for variability between the expression of different genes. • There are many (many!) other sources of variability • Most microarray analysis is about trying to normalise these sources of variability, leaving biological variability Artifacts The Jolly Green Giant The Yellow Splodge Peril Space Invaders Solutions • Removing Sections • Background Subtraction • Start Again Feature Recognition • Not all spots are equal – different sizes, different shapes. • Identifying the exact scope of the spot on an array can therefore be hard. • Often solved in the initial detection of spots. Spot Detection The Doughnut A general disaster The basic solution to this is to not use circular spots for detection. There are a variety of edge detection algorithms, or manual tools which work. An experiment RT with Cy3 dCTP Two Samples Combine into single sample RT with Cy5 dCTP Hybridise to Microarray Channel Variability • Cy3/Cy5 dyes have different properties. • So do the lasers at different frequencies. • So do the photomultipliers which detect them. Within Slide Variability • Slides often have imperfections, either from spots, or background • Gaps are not uncommon, neither are chromatic effects Inslide Normalisation Between slide variability • Results between different slides are not directly comparable. • Results between different experiments are not directly comparable. Further work Smith JR, Choi D, Chipps TJ et al. Unique gene expression profiles of donor matched human retinal and choroidal vascular endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007;48:2676-2684. Chi JT, Chang HY, Haraldsen G et al. Endothelial cell diversity revealed by global expression profiling. Pro Nat Acad Sci 2003;100:10623-10628.