* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10, part A
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
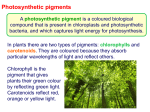
11/12/12 Ch 10: Plant Metabolism Photosynthesis In general Types of chemical reactions in metabolism: photosynthesis or 1 11/12/12 Types of chemical reactions in metabolism: redox reactions (moving electrons) oxidized (H atoms reduced carrying e-s) How enzymes work (see also Ch 2 p25-6) without enzyme with enzyme Enzyme reactions 2 11/12/12 One of the circles of life (but not everything can be recycled; eg: energy) Note: plants do both photosynthesis AND cellular respiration Anabolism: Producers some bacteria, protists, plants archaea & bacteria (some bacteria don’t produce O2) Chlorophyll a heme hydrophobic tail 3 11/12/12 Absorption spectra of chlorophylls and a carotenoid Why leaves appear green Algae (K: Protista) Group PS Pigments Reds chl a, phycobilins, carotenoids Dinoflagellates chl a & c (usually), carotenoids Diatoms chl a & c, carotenoids Xanthophytes chl a & c, carotenoids Chrysophytes chl a & c, carotenoids Coccolithophorids chl a & c, carotenoids Browns chl a & c, carotenoids Euglenoids chl a & b, carotenoids Greens chl a & b, carotenoids Photosynthetic structures: Leaf, mesophyll cells and chloroplasts 4 11/12/12 Photosynthetic structures: Photosystems structures with pigments (held by proteins) arranged to catch light A closer look antenna (of pigments) aka. light harvesting complexes PSI has reaction center P700 PSII has reaction center P680 Cyclic photophosphorylation makes ATP involves just PS I 5 11/12/12 Non-cyclic photophosphorylation: makes ATP & NADPH & O2 involves PS I and PS II ets How is ATP actually made? Photophosphorylation Electron transport system/chain and chemiosmosis What are the ATP & NADPH for? Calvin cycle = carbon fixation (making sugars) 12 x 3C 2 x 3C 10 x 3C 12 x 3C Rubisco (6 x 5C) 6 11/12/12 Photorespiration = Rubisco makes a mistake (GA3P) mistake (GA3P) Not useful Alternative to standard C3 photosynthesis: C4 photosynthesis pumps CO2 (in C4 acid) to Rubisco in bundle sheath cells Kranz anatomy (C4 acid formed) Alternative to standard C3 photosynthesis: CAM - when you can t keep your stomates open during the day store up CO2 (in C4 acid) at night (C4 acid formed) 7