* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download All plants don`t occur everywhere. Different plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
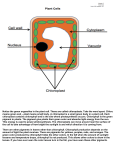
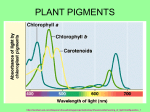
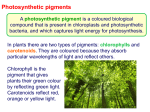
Why Leaves Change Color in the Fall All plants don’t occur everywhere. Different plants are NATIVE to different places. Rainforest plants are often used as house plants in North America because the house is a 'constant' temperature year round. In addition, ornamentals in the yard are often bred to have 'everlasting' leaves. This means they lose leaves year round and not all in one season (it also means our yards aren't quite so bare in the winter - they are also planted around the foundations of houses or in flowerbeds!) and bred to have fairly uniform color year round. One exception to this is 'burning bush' or 'nandina' which turn red/orange in fall/winter but are yellow/green the rest of the year. Subject: FYI - why leaves change color in fall Question: Why Do Leaves Change Color in the Fall? Answer: Well, it is a two part answer – Reasons include both pigments and temperature. PIGMENTS - When leaves appear green, it is because they contain an abundance of chlorophyll. There is so much chlorophyll in an active leaf that the green masks other pigment colors. Light regulates chlorophyll production, so as autumn days grow shorter, less chlorophyll is produced. The decomposition rate of chlorophyll remains constant, so the green color starts to fade from leaves. At the same time, surging sugar concentrations cause increased production of the pigment anthocyanin. Leaves containing primarily anthocyanins appear red. Carotenoids are other pigments found in some leaves and is not dependent on light, so levels aren't diminished by shortened days. Carotenoids can be orange, yellow, or red, but most of these pigments found in leaves are yellow. Leaves with good amounts of both anthocyanins and carotenoids appear orange. Leaves with carotenoids but little or no anthocyanin will appear yellow. In the absence of these pigments, other plant chemicals also can affect leaf color. An example includes tannins, which are responsible for the brownish color of some oak leaves. TEMPERATURE - Temperature affects the rate of chemical reactions, including those in leaves, so it plays a part in leaf color. However, in temperate zones it's mainly light levels that are responsible for fall foliage colors. Sunny autumn days are needed for the brightest color displays, since anthocyanins require light. Overcast days will lead to more yellows and browns. Also, sunny warm days with cool / almost cold nights seem to speed up or help the color 'change' and bring the most color to leaves.