* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endosymbiotic Theory
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
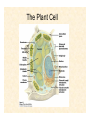
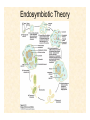
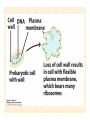
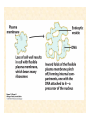
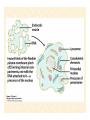
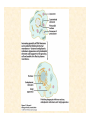
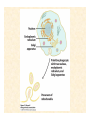
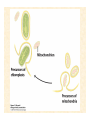
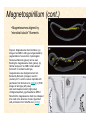
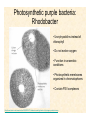
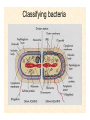
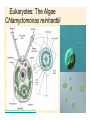
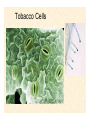
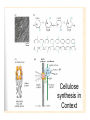
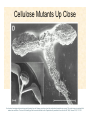
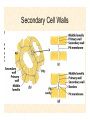
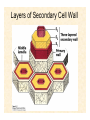
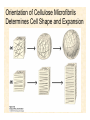
The Endosymbiotic Theory Possible Origins of Eukaryotes The Plant Cell Endosymbiotic Theory Lab 4. The Prokaryote and the Plant Cell Today in Lab... • Looking at exceptions to the prokaryotes-arewithout-organelles rule • Gram-staining bacterial and environmental samples • Examining a green algae • Looking at moss cells and making protoplasts • Revisiting the chromoplast (hopefully better samples) and pigment distribution in various plant species • Looking at cell types in Tobacco plants (Nicotiana tabacum and N. benthamiana) • Finally, we will examine plant cells in context using Brassiceae and a polychromatic stain Some bacteria DO have organelles(!) e.g. the acidocalcisomes in Agrobacterium Electron microscopy and x-ray microanalysis of wholeA. tumefaciens. D–H, electron micrographs of intact bacteria (D–F) and volutin granule fractions (Gand H). Arrows show vacuoles, some containing an electrondense material in the periphery (D and E), some completely occupied by electron-dense material (E, arrowhead), and some apparently empty (F, arrowhead). Fractions show almost empty vacuoles containing an electrondense material in their periphery (G and H). A membrane is clearly seen enclosing the vacuoles (arrow in E; arrowheads in F, G, andH). Bars, 0.1 μm. Seufferheld M, et al. (2003) JBC, 278, 29971-29978. Magnetospirillummagnetic bacteria! Figure 1. Features of magnetosomes. (a) A transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of sectionedMagnetospirillum magneticum AMB-1 reveals the presence of a chain of electron-dense magnetite crystals [Image courtesy of T. Beveridge, reprinted with permission from Komeili et al. (2004)]. (b) Sections from an electron cryotomographic image of AMB-1 show that magnetosomes are invaginations of the inner cell membrane at various stages of biomineralization. (c) The same study shows the presence of filaments parallel to the magnetosome chain [Images in b and c courtesy of Z. Li and G. Jensen reprinted with permission from Komeili et al. (2006)]. Magnetospirillum (cont.) • Magnetosomes aligned by “microbial tubulin” filaments Figure 4. Magnetosome chain formation. (a) Image of an AMB-1 wild-type cell generated by segmentation of an electron cryotomogram. Numerous filaments (green) can be seen flanking the magnetosome chain (yellow). (b) Similar analysis of an AMB-1 strain deleted formamK. In contrast to wild type, magnetosomes are disorganized and not flanked by filaments. [Images in a and b courtesy of Z. Li and G. Jensen reprinted with permission from Komeili et al. (2006)]. (c) TEM images of wild-type (left panel) and mamJ deletion mutant (right panel) of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense MSR-1. Note that the magnetosome chain has collapsed into a ball in the absence of mamJ [reprinted with permission from Scheffel et al. (2006)]. Photosynthetic purple bacteria: Rhodobacter • Use phycobilins instead of chlorophyll • Do not evolve oxygen • Function in anaerobic conditions • Photosynthetic membranes organized in chromatophores • Contain PSII complexes http://www.bbsrc.ac.uk/news/archive/2009/090617-f-bacteria-make-light-work-of-hydrogen-production.aspx Cyanobacteria: Synechocystis sp The blue-green “algae” • The ancestor of the modern day chloroplast • Possesses both PSI and PSII • Has chlorosome compartments that contain thylakoid membranes 1000x Though we’ve been looking at “exceptional” bacteria, all prokaryotes can be classified according to a basic cellular determinant: Their cell wall. Classifying bacteria The Gram stain Moving onto the Eukaryotes... Eukaryotes: The Algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii http://www.uni-jena.de/en/DFG_Research__Group_1261.html Physcomitrella patens: a Moss Protoplast Carrot chromoplasts Tobacco Cells Cell Wall Lecture Supplements Scanning Electron Micrograph of Plasma Membrane with clusters of Rosettes Giddings TH Jr, Brower DL, Staehelin LA. J. Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):327-39. Close up of Rosettes occurring in PM Cellulose synthesis in Context What happens when things go wrong? Cellulose Mutants: Arabidopsis thaliana Left to right: Columbia wild type, low lignin mutant, low cellulose mutant Talbot JM, KK Treseder. In press. Lignin, cellulose, and N interactions are major drivers of litter chemistry-decay relationships. Ecology. DOI: 10.1890/110843.1. Cellulose Mutants Up Close Chapter 3: The Plant Cell and the Cell Cycle A colourised scanning electron micrograph showing how cell shapes go astray when the mechanical properties are wrong. The main image is a mutant that makes less cellulose. The inset is the wild type with normal cellulose levels. Reprinted with permission from Arioli et al 1998, Science 279, 717-720. Complexity of the Cell Wall Secondary Cell Walls Layers of Secondary Cell Wall Orientation of Cellulose Microfibrils Determines Cell Shape and Expansion Bay Area Biofuel Companies