* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
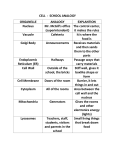
7.12D Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole • Structure: Flexible Membrane with small holes, Surrounds cells (outside layer for animal cells, just inside cell wall for plants) • Function: Controls what goes in and out of cell (transports material) & Holds in cytoplasm • Analogy: It is like the bright orange flexible fencing around construction sites because it protects the work site while still allowing things to go through. • Structure: are free in the cytoplasm and often attached to the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. • Function: Protein production for the Cell • Analogy: a factory that makes proteins Structure: Gel-like fluid made mostly of water The material inside the membrane Function: • Holds organelles • keeps cell flexible • maintains shape of cell Analogy: It is like the water in a swimming pool because all the stuff that happens in the pool happens in the water. The water supports the swimmer like cytoplasm supports organelles Structure: Bean inside shape with many layers Function: Transforms energy (from nutrients and Oxygen) for cells to use Analogy: Mitochondria act like a power plant because they both transform other materials to make energy. Structure: Large and round, will usually be located towards the middle of the cell. Membrane bound (eukaryotic) Function: Contains genetic material (DNA), controls cellular activities Analogy: The nucleus is like the brain of a human because the brain controls the actions of the body like the nucleus controls the cell. Structure: Flat, folded around the nucleus membrane, usually Function: Makes proteins for the cell. Internal delivery system. Analogy: ER is like a factory that produces goods and ships what they have made. Rough ER – is involved in some protein production, protein folding, quality control and dispatch. It is called ‘rough’ because it is studded with ribosomes Smooth ER - storage and metabolism of carbohydrates, synthesis and transport of lipids Structure: Stacked membranes Function: Packages and delivers materials made from ER. In plants, the Golgi made cell wall material. Analogy: Golgi bodies are like FedEx because they package and ship materials around and out of cell. Structure: small and round, usually more found in animal cells. Can move within cells. Function: Digestion of cellular waste. Recycles old cell material to make new molecules. Analogy: Lysosomes are like your digestive system because both can break apart larger materials to make new molecules. Structure: small and round in animal cells, usually a single large bag-like structure in plants Function: stores water and nutrients, aids(helps) in cellular digestion. In plants it works with the cell wall for cell support (turgor pressure). Analogy: A canteen is like a vacuole because both are used to store water. Structure: green, bean plant cells shaped – found only in Function: contains chlorophyll that makes photosynthesis possible Analogy: Kitchens are like chloroplast because both make “food” for organisms. Structure: rigid material that forms the outer layer of plant cells. Function: gives plant cells support and protects cell’s interior. Analogy: Walls of a building are like a cell wall because both are used for support.