* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STAGES OF MITOSIS
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
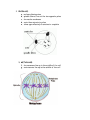
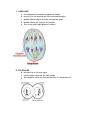
PHASES OF MITOSIS The cell cycle (20 hours) 1. INTERPHASE: a. this is what the cell looks like in its normal phase b. it is not considered a phase of mitosis c. it is a period of intense metabolic activity prior to mitosis d. it consists of 3 phases: 1. G1- cell prepares for replication and organelles reproduce 2. S- synthesis of DNA, replication of genetic material 3. G2- last stage of interphase 2. PROPHASE: a. nucleus disintegrates b. spindle fibers form at the two opposite poles c. chromatin condenses d. centrioles migrate to poles e. takes approximately 6 minutes to complete 3. METAPHASE: f. chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell g. centromeres line up in the middle of the cell 4. ANAPHASE: a. chromosomes (centromeres separate slowly) b. arms of the chromatids pull the centromeres apart c. spindle fibers help to pull the cenromeres apart d. spindle fibers get shorter and thicker e. this is the most rapid phase of mitosis 5. TELOPHASE: h. nucleus starts to form again i. cytokinesis occurs and the cell divides j. two daughter cells are formed identical to the parent cell






![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)