* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the cell lab2 part 1 and 2
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
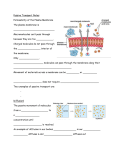
Human Biology Practical part Technical college of health Human biology First year Part 1 The cll Lab.2 cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Discovery of Cells: _ Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) – Observed sliver of cork – Saw “row of empty boxes” – Coined the term cell Cell Theory • (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden “ all living things are made of cells” • (50 yrs. later) Rudolf Virchow “all cells come from cells” Cell Size: Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane: consist of double layer of phospholipids and proteins Membrane Proteins: 1. Channels or transporters – Move molecules in one direction 2. Receptors – Recognize certain chemicals 3. Glycoproteins – Identify cell type 4. Enzymes – Catalyze production of substances Cell Walls: • Found in plants, fungi, & many protists • Surrounds plasma membrane Lab experiment and activity 1- Preparing direct and indirect stained slides for different type of cell including human skin, mouth swab, and plant cell 2. Examining the checking egg under microscope 3. Drawing the both animal and plant cell in the lab Human Biology Practical part Part 2 Movement Across the Plasma Membrane: Lab.2 Movement Across the Plasma Membrane: -A few molecules move freely: Water, Carbon dioxide, Ammonia, Oxygen – Carrier proteins transport some molecules – Proteins embedded in lipid bilayer – Fluid mosaic model – describes fluid nature of a lipid bilayer with proteins Diffusion Diffusion through Cell Boundaries • Particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration • No energy is required Osmosis • Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane Isotonic "ISO" means the same Concentration of solutes (salts) is the same inside and outside of cell. • Water flows in and out in equal amounts • No effect on cell Hypertonic “Hyper” means more Concentration of solutes is more outside the cell than inside • Water flows out of cell • The cell shrivels and may die. • This is why it is dangerous to drink sea water • This is also why "salting fields" was a common tactic during war, it would kill the crops in the field, thus causing food shortages. Hypotonic "HYPO" means less Concentration of solutes is less outside the cell than in • Water flows in • The cell swell with water and becomes “turgid” Active Transport • Carried molecules by protein pumps found in the membrane • Energy is required Lab experiment and activity 1- Preparing normal saline, hypertonic and hypotonic solution. 2. Demonstrating the cell in the hypertonic and hypotonic solution. 3. Drawing plasma membrane of the cell in the lab. Any questions