* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA to Protein Synthesis Internet Quest
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
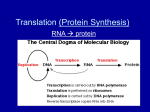
Name Date Period _____ DNA to Protein Synthesis Internet Quest Purpose: To give you a better understanding of how the message found on a molecule of DNA is used to build a protein. Site 1 – DNA and RNA Comparison 1. Read the information presented on the website and organize it in the following chart. Nucleic Acid # of “strands” Sugar Nitrogen Bases Size Comparison Location in Cell DNA RNA 2. Identify the function of the three types of RNA molecules. a. Ribsosomal RNA (rRNA) – b. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – i. Describe the tiny ribosome organelle: c. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – 3. Generally speaking, list the transcription steps which allow a cell to go from DNA to building a protein. DNA of a specific gene “unzips”….. Site 2 – Protein Synthesis Illustrations 4. Read and click slides 1 – 4. Use slide 4 to draw a picture of an unzipped and exposed gene being used to create a molecule of mRNA during transcription. Be sure to label both the DNA and RNA sequences, pairing the correct complementary bases. 5. How does the mRNA molecule leave the nucleus? 6. Click and read slides 1 – 8. Use slides 8 and 9 to help you draw several transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules. Be sure to label the anticodon, the binding site and the attached amino acid. 7. Click and read slides 9 – 14. Using slide 14, illustrate how the mRNA molecule is “read” and used to build a polypeptide chain (protein) during translation. Label the following terms: ribosome, mRNA, tRNA, codon, anticodon, amino acid, growing polypeptide chain. 8. What happens to the mRNA molecule when protein production is complete? Transcription & Translation Practice 9. Practice transcription by building a molecule of RNA by using DNA as a “template.” Give the complementary sequence below. DNA Sequence: T A C C C G A G G RNA Sequence: Site 3 – Translating an mRNA sequence You can translate an mRNA sequence into an amino acid chain by using a _________ chart. (see below) The mRNA language has no spaces between the words, and the beginning of the mRNA sentence is indicated by a particular three-nucleotide sequence, _____________ (the amino acid methionine), which is called a _________ codon." Translation ends at the "_________" codons: _______, UAG, and ________. 10. Match the complementary anticodons on the tRNA molecules. Identify the coded amino acids below. a. mRNA codon: A U G i. What is the complementary tRNA anticodon? ii. This codon signals for which amino acid? b. mRNA codon: G G C i. What is the complementary tRNA anticodon? ii. This codon signals for which amino acid? c. mRNA codon: U C C i. What is the complementary tRNA anticodon? ii. This codon signals for which amino acid? 11. How do you know when the protein being built is complete? Link 5 -‐ Final Analysis 12. Use the diagram in this link. Draw this diagram which illustrates the entire process (DNA àRNA àProtein). Label all major parts!! Dr. Harvey says thanks for the journey…….