* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download aldehydes and ketones
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Discodermolide wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Diels–Alder reaction wikipedia , lookup
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stille reaction wikipedia , lookup
Ene reaction wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
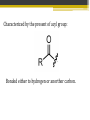
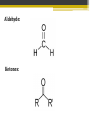
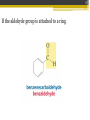
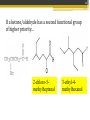
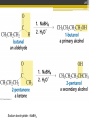
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES BY: SALEHA SHAMSUDIN Introduction: Aldehyde and Ketones nomenclature, physical and chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Reactions Aldehydes and Ketones: The concept of aldehydes and ketones: Relative reactivity of the carbonyl group, oxidation reaction of aldehydes and ketones. Ketones reduction reaction. Nucleofilic addition reaction. Grignard Reagent. Aldehydes and ketones reactivity in nucleofilic addition reaction. Reactions: Claisen condensation, Aldol condensation, Michael reaction, Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction. Characterized by the present of acyl group: Bonded either to hydrogen or anorther carbon. Aldehyde: Ketones: Naming the Aldehyde and Ketone For an aldehyde, the –e ending of the corresponding alkane name is replaced by –al. With ketone, the –e ending of an alkane is replaced by -one in the longest continous chain containing the carbonyl group. 6 Nomenclature of Aldehydes 3 p/s: the 1st position is given to carbonyl compound 2 1 p/s: α-carbon or β-carbon? 8 If the aldehyde group is attached to a ring, 9 Nomenclature of Ketones p/s: Give the ketone the smaller number. The carbonyl is assumed to be at the 1-position in cyclic ketones: 11 If a ketone/aldehyde has a second functional group of higher priority… 2-chloro-5methylheptanal 3-ethyl-4methylhexanal 12 If a compound has two functional groups, the one with the lower priority is indicated by its prefix: Physical properties Have higher boiling points than hydrocarbon because they are more polar and the forces between molecules are stronger. They have lower boiling point than alcohols?, why? They are more soluble than hydrocarbons but less soluble than alcohols in water. Relative reactivity of the carbonyl group 15 The partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon causes the carbon to be attacked by nucleophiles: An aldehyde has a greater partial positive charge on its carbonyl carbon than does a ketone: 16 Aldehydes Are More Reactive Than Ketones • Steric factors contribute to the reactivity of an aldehyde. • The carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde is more accessible to the nucleophile because the hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde is smaller than the second alkyl group to carbonyl carbon of a ketone. • Ketones have greater steric crowding in their transition states, so they have less stable transition states. • Both factors cause ketone to be less reactive than aldehyde (MS776) Alkyl group stabilized the reactant 18 The reactivity of carbonyl compounds is also related to the basicity of Y–: (lone pair of an atom) Less able to share their lone pair with carbonyl carbon Carbonyl compound other than aldehyde and ketone have a lone pair on an atom which attached to carbonyl compound group that can be shared by resonance edonation. This makes the carbonyl carbon less electron deficient and less reactive. How aldehydes and ketones react 20 Carboxylic acid derivatives undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions with nucleophiles: 21 Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with nucleophiles: This is an irreversible nucleophilic addition reaction if the nucleophile is a strong base 22 A reversible nucleophilic addition reaction: Nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction If the nucleophile has a lone pair and there is enough acid in the solution to protonate the tetrahedral compound, water can be eliminated. Reversible reaction. ? 24 Formation of a New Carbon–Carbon Bond Using Grignard Reagents Grignard reagents react with aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acid derivatives Grignard reagents are used to prepare alcohols: 25 26 Mechanism for the reaction of an ester with a Grignard reagent: Undergo two successive reactions : (1) nucleophilic additionelimination reaction; (2) Nucleophilic addition reaction Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds with Hydride Ion Hydronium ion Hydride ion Alkoxide ion Ketone or aldehyde is reduced to primary or secondary alcohol 27 28 Sodium borohydride –NaBH4 The reactions of acyl chloride, esters and carboxylic acids with hydride ion -Product intermediate is an aldehyde -Undergo two successive reactions with hydride ion 30 Mechanism for the reaction of an acyl chloride with hydride ion: 31 Mechanism for the reaction of an ester with hydride ion: methanol Alkoxide ion Esters and acyl chlorides undergo two successive reactions with hydride ion and Grignard reagents By Lithium aluminium hydrate (LiAlH4) 32 Hydrogen cyanide adds to aldehydes and ketones to form cyanohydrins: excess Excess cyanide is used.