* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student Guide to Animal and Plant Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
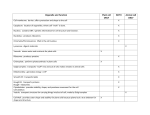
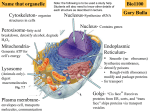
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Student Guide to Animal and Plant Cells Directions: You will turn this assignment in. Copy down the name of each cell part and what it does in your on a clean sheet of paper. As you copy down the information about each part, add that part to your model(s). Parts of a eukaryotic cell: 1. Cell wall: provides strength and support to the cell membrane. Found in plant cells only. 2. Cell membrane: covers and protects the cell’s surface. 3. Cytoskeleton: the cell’s skeleton. A web of proteins that helps shape cells and helps cells move. Microtubules are part of the cytoskeleton that look like tubes. Microfilaments are part of the cytoskeleton that look like thin strings. 4. Nucleus: holds DNA. DNA is made up of chromosomes. The nucleolus is a dark spot in the center of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. 5. Ribosome: makes proteins. There are many ribosomes in each cell. 6. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): produces, processes and transports proteins and lipids. The rough ER has ribosomes on its surface. The smooth ER does not. 7. Mitochondria: breaks down food to make power for a cell. There are many mitochondria in each cell. 8. Chloroplast: catch sunlight and use it to make food. There are different types of plastids in cells. There are many chloroplasts found in each cell. Found in plant cells only. 9. Golgi complex: packages and transports proteins and lipids that come from the ER. 10. Lysosome: digests anything that is not needed or is not supposed to be in a cell. Found more in animal cells than in plant cells. There are many lysosomes in each cell. 11. Vacuole: large storage space in a cell. Bigger in plant cells than in animal cells. 12. Centrioles: used when cells copy themselves. (Your plant cell model does not have centrioles, but plant cells do have centrioles.) Once you have finished both models, raise your hand and show Mrs. Hobbs. Once you have shown Mrs. Hobbs, draw both cells in your notes, and label each part. Create a Venn diagram in your notes. Use the diagram to answer the question: what cell parts are found in both plant and animal cells; what parts are found in only plant cells or only animal cells?