* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint version
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
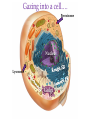
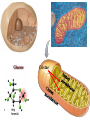
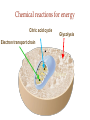
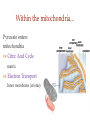
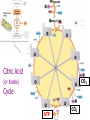
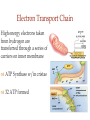
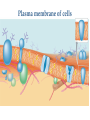
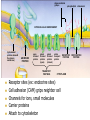
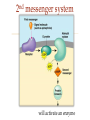
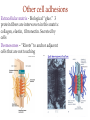
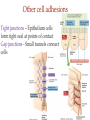
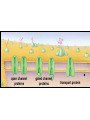
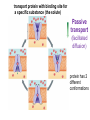
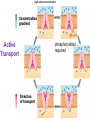
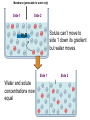
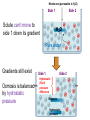
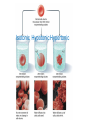
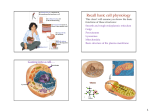
(a) Chemical level: a molecule in the membrane that encloses a cell (b) Cellular level: a cell in the stomach lining (c) Tissue level: layers of tissue in the stomach wall (d) Organ level: the stomach (e) Body system level: the digestive system (f) Organism level Recall basic cell physiology This class I will assume you know the basic functions of these structures: Smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum Golgi Peroxisomes Lysosomes Mitochondria Basic structure of the plasma membrane Gazing into a cell…. Peroxisome Nucleus Lysosome Golgi Cristae Glycolysis can occur with or without oxygen Yet, aerobic respiration yields more energy from glucose and occurs in the mitochondria Chemical reactions for energy Citric acid cycle Glycolysis Electron transport chain Cytosol Making ATP First, glycolysis – then either: Aerobic Pathway Anaerobic Pathway Citric acid cycle Electron transport chain Fermentation Within the mitochondria... Pyruvate enters mitochondria Citric Acid Cycle matrix Electron Transport Inner membrane (cristae) Pyruvate Acetyl-CoA Citric Acid CO2 (or Krebs) Cycle ATP CO2 Where does weight ‘go’ when someone loses weight? Electron Transport Chain High energy electrons taken from hydrogen are transferred through a series of carriers on inner membrane ATP Synthase w/in cristae 32 ATP formed Free radicals from ETC A by-product of ETC is the production of abnormal versions of O2 (O2-, O2--) These molecules are highly reactive and produce “free radicals”, which contribute to aging and some diseases. Energy Harvest Glycolysis (from one glucose) 2 ATP 2 NADH (makes 4 ATP in ETC) Citric Acid Cycle 2 ATP plus NADH, FADH2 for ETC Electron Transport Chain 28 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation Anaerobic conditions Aerobic conditions Lactic acid myth Lactic acid (really lactate) isn’t the cause of muscle fatigue and soreness Lactate leaves muscle, enters blood and is used elsewhere for ATP production (using O2 ) Lactate threshold Interval training uses periods of training above and below the L threshold. High intensity portions stimulate your body to produce enzymes that speed the use of lactate fuel (MCT1 carrier protein) Plasma membrane of cells oligosaccharide groups phospholipid cholesterol EXTRACELLULAR ENVIRONMENT (cytoskeletal proteins beneath the plasma membrane) ADHESION PROTEIN open channel protein gated channel protein (open) gated channel protein (closed) TRANSPORT PROTEINS active transport protein RECEPTOR PROTEIN CYTOPLASM Receptor sites (ex: endocrine sites) Cell adhesion (CAM) grips neighbor cell Channels for ions, small molecules Carrier proteins Attach to cytoskeleton RECOGNITION PROTEIN Membrane receptors Binding to the receptor will: Open or close channels for ions (Na+, K+, Ca++) Transfer a signal to 2nd messenger to trigger events in the cell 2nd messenger system will activate an enzyme Other cell adhesions Extracellular matrix - Biological “glue.” 3 protein fibers are interwoven in this matrix: collagen, elastin, fibronectin. Secreted by cells Desmosomes – “Rivets” to anchor adjacent cells that are not touching Other cell adhesions Tight junctions – Epithelium cells form tight seal at points of contact Gap junctions - Small tunnels connect cells open channel proteins gated channel proteins transport protein transport protein with binding site for a specific substance (the solute) Passive transport (facilitated diffusion) protein has 2 different conformations high solute concentration Concentration gradient phosphorylation required Active Transport Direction of transport Membrane (permeable to water only) Side 1 Side 2 Solute can’t move to side 1 down its gradient but water moves H2 O Side 1 Water and solute concentrations now equal Side 2 Membrane (permeable to H2O) Side 1 Solute can’t move to side 1 down its gradient Side 2 H2 O Pure water Gradients still exist Osmosis is balanced by hydrostatic pressure Side 1 Side 2 Hydrostatic (fluid) pressure difference Osmosis Hydrostatic pressure Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic