* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cscope Specialized Cell Structures ppt notes
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
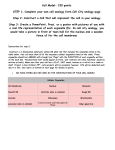
Cell Wall Description: Rigid outer layer Outside of cell membrane Function: Support Protection Helps cell maintain its shape Analogy Cell Membrane Description: Outside covering of cell made of lipid bilayer Function: Barrier between cell and its environment Controls what substances can enter or leave the cell Provides support and protection, especially in cells without a cell wall Analogy Ribosomes Description: Made of protein and RNA Very small, spherical shaped Function: Make proteins Analogy Cytoplasm Description: Jelly-like substance that fills the cell and surrounds the organelles Function: Fills space between organelles Contains materials needed by the organelles Analogy Flagella Description: Long, thread-like extension of a cell Function: Helps cell move Analogy Cilia Description: Short, hair-like projection on the cell surface Function: Used to sweep away things from the cell surface or help the cell move through fluid Analogy Nucleus Description: Core, central portion of cell Function: Contains genetic information (DNA) Directs cell activities Analogy Nuclear Membrane Description: Double-layer membrane surrounding the nucleus Function: Separates nucleoplasm from cytoplasm Analogy Nucleolus Description: Round structure within nucleus Made of protein and RNA Function: Makes ribosomes Analogy Chloroplast Description: Oval or bean shaped structure with green color Function: Helps capture sunlight to produce food (energy) for plants Analogy Golgi Apparatus Description: Flattened sacs called cisternae Function: Modifies and packages materials created in the cell for transport (inside or outside of the cell) Analogy Lysosome Description: Small sacs Function: Use digestive enzymes to breakdown old/worn-out organelles, viruses or bacteria, and/or food particles Analogy Mitochondrion Description: Spherical or rod-shaped Inner and outer membranes Function: Converts sugars into ATP (energy) for the cell Analogy Plastid Description: Double-membrane bound organelle Function: Involved in food storage; function depends mostly upon which pigments are present Analogy Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Description: System of membranous tubes and sacs with ribosomes on the surface (making it appear rough) Function: Helps make and transport new proteins to Golgi apparatus or outside of the cell Analogy Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Description: System of membranous tubes and sacs Function: Makes lipids Creates and stores steroids Stores ions that cells might need Metabolizes carbohydrates Analogy Vacuole Description: Sacs: smaller in animal cells, larger in plant cells Function: Store a variety of things such as water, nutrients, or waste products Analogy Vesicle Description: Small sacs Function: Stores, transports, or digests materials within the cell Analogy Levels of Organization in Ecology What is the correct level of organization (think back to the card activity from our previous class)? atom molecule organelle cell tissue organ organ system organism population community ecosystem Wikimedia Commons free use from NASA