* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MADANIA (High School) Grade 10-Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
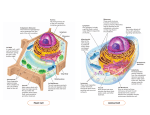
Name : ________________ Class : 10____ Day/Date : ________________ MADANIA (High School) Grade 10-Biology-Handout 2 Cell Structure 09 / 08 / 2010 All living organisms on Earth are divided in pieces called cells. There are smaller pieces to cells that include protein and organelles. There are also larger pieces called tissues and systems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and succesful on Earth. A main purpose of a cell is to organize. Cells hold a variety of pieces and each cell has a different set of functions. There are two kinds of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. All cells have several basic features in common: They are bounded by a plasma membrane They contain a semifluid substance called the cytosol They contain chromosomes They all have ribosomes Plasma membrane The cell membrane is not one solid piece. Compounds called proteins and pho spholipids make up most of the cell membrane. Cytoplasm Cytoplasm or cytosol is the fluid that fills a cell. The cytoplasm has many different molecules dissolved in solution. You will find enzymes, fatty acids, sugars and amino acids that are used to keep the cell working. Ribosomes Cells need to make proteins. Ribosomes are the protein synthesizers of the cell. They might be found in cytoplasm and rough endoplasmic reticulum. Chromosomes Chromosomes are made up of DNA. Segments of DNA in specific patterns are called genes. Your genes make you who you are. Chromosomes and genetic material can be found in nucleus. In prokaryotes, DNA flotas in the cytoplasm in an area called nucleoid. Chromosemes are usually found in pairs. Cell Nucleus The cell nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. The nucleus is not always in the center of the cell. It will be a big dark spot somewhere in the middle of cytoplasm (cytosol). Not all cells have a nucleus. Take for example prokaryotic cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Endoplasmic reticulum functions as the packaging system. It does not work alone. The ER works closely with Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, RNA, mRNA and tRNA. There are two types of ER: rough and smooth ER. Smooth ER acts as a storage organelle. It is important in the creation and the storage of steroids. Rough ER S1/W5/Handout2/G.10/DIN/Biology/2010-2011 Page 1 has ribosomes attached. Ribosomes are very important in the synthesis and packaging of proteins. Some of the proteins might be used in the cell and some are sent out. As the ribosome build the amino acid chain, the chain is pushed into the ER . When the protein is complete, the rough ER pinches off a vesicle (small membrane). The vesicle can move to the cell membrane or Golgi apparatus. Golgi apparatus Golgi apparatus or golgi complex gathers simple molecules and combine them to make more complex molecules. It then takes those big molecules, packages them in vesicles, and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. Golgi apparatus also builds lysosomes (cell digestion machine). Golgi apparatus receives transition vesicles contains of proteins from endoplasmic reticulum. After the Golgi does its work on the molecules inside the vesicles, a secretory vesicle is made and released into the cytoplasm. From there, the vesicle moves to the cell membrane and the molecules are released out of the cell. Vacuoles Vacuoles are storage bubbles found in cells. They are found in both animal and plant cells but are much larger in plant cells. Vacuoles might store food or any kinds of nutrients a cell might need to survive. They can even store waste products so the rest of the cell is protected from contamination. Mitochondria Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They are organelles that act like a digestive system that takes in nutrients, breaks them down and creates energy for the cell. Mitochondria have two membranes. The outer membrane covers the organelle and its content. The inner membrane folds over many times (cristae). The fluid inside of the mitochondria is called the matrix. S1/W5/Handout2/G.10/DIN/Biology/2010-2011 Page 2 Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotic celss are small, relatively simple cells. They do not have a nucleus. A prokaryotic cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane and is usually encased in a rigid cell wall. Eukaryotic Cell Eukaryotes are distinguished by the presence of a true nucleus. Eukaryotic organelles fall into four functional groups. S1/W5/Handout2/G.10/DIN/Biology/2010-2011 Page 3 Animal Cell S1/W5/Handout2/G.10/DIN/Biology/2010-2011 Page 4 Plant Cell • A plant cell has some structures that an animal cell lacks: Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall. S1/W5/Handout2/G.10/DIN/Biology/2010-2011 Page 5