* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
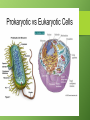
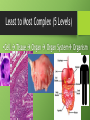
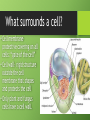
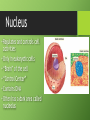
Cells Cell Size • We need a microscope to see most cells. Cork cells Plant cell Onion cell Animal cell Cell Theory •All organisms are made of one or more cells •The cell is the basic unit of all living things •All cells come from existing cells Parts of a Cell • All cells have these 3 parts: 1.Cell Membrane: Layer that covers cell’s surface and acts as a barrier between inside of cell and its environment 2.Cytoplasm: The fluid inside a cell 3.DNA: The genetic material that carries information needed to make new cells/organisms Copy this chart in your composition book. Work with your group to complete the chart. Two Types of Cells 1.Prokaryotes •Single-celled organisms •Smaller •Do NOT have a nucleus or organelles •Ex: bacteria, archaea 2. Eukaryotes •Can be single or multi-cellular •Larger •Have a nucleus and organelles •Ex: animals, plants, fungi Homeostasis • Cells work together to maintain homeostasis. Cells have different functions. • Homeostasis = stable environment in your body; balance • Your body maintains its homeostasis even if outside conditions are changing. Levels of Organization • Tissue- group of similar cells working together • Organ- two or more tissues that work together • Organ system- two or more organs that work together • Organism- has multiple organ systems that work together to maintain homeostasis in the entire body Least to Most Complex (5 Levels) • Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism What surrounds a cell? • Cell membraneprotective covering on all cells: “gate of the cell” • Cell wall- rigid structure outside the cell membrane that shapes and protects the cell • Only plant and fungus cells have a cell wall. Cytoskeleton •Proteins in the cytoplasm •Keeps the cell membrane from collapsing •Helps some cells move Organelles •Cells are made of different parts (organelles). •Each organelle has a different function to help the cell. •Located in the cytoplasm Ribosomes •Make proteins •Small; not covered by a membrane •In eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells •Can float freely in cytoplasm or be attached to something else Nucleus • Regulates and controls cell activities • Only in eukaryotic cells • “Brain” of the cell • “Control Center” • Contains DNA • Often has a dark area called nucleolus Nuclear Membrane •Protects the nucleus •Allows substances to pass in and out of the nucleus •“Gate of the nucleus” Chromosomes •where DNA is located in the nucleus Mitochondria • Produces energy by breaking down sugar • “Powerhouse of the cell” • A cell can have multiple mitochondrion Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Produce and transport proteins and lipids • folded • Smooth- no ribosomes • Rough- has ribosomes Golgi Complex/Apparatus •Packages and distributes proteins Vacuoles •Store water and other materials Lysosomes •Digest and get rid of waste •Found mostly in animal cells Chloroplasts •Contains chlorophyll, which captures energy from sunlight and uses it to produce food for the cell •Only in plant cells