* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
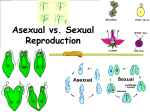
Chapter 6 Reproduction and Gene Function Asexual Reproduction: A Result of Mitosis • Asexual reproduction is reproduction by mitotic cell divisions. • An amoeba is an organism that reproduces asexually. • An amoeba simply grows and then divides in to two organisms! Asexual Reproduction • Budding • Yeast cells reproduce asexually by budding. • A bulge forms on the cell and it eventually breaks off in the form of a new yeast cell. • This is by mitosis. Asexual Reproduction • Regeneration • Some worms have the ability to reproduce through regeneration. • If cut in two pieces, both pieces will eventually grow into new worms. Asexual Reproduction • Spores • Many organisms produce spores by mitosis. • Mold does this. How Genes Function • In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick worked out a model for the structure of DNA! • DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. • Their model looked like a twisted ladder. • The ladder contains units called nucleotides. How Genes Function • There are three parts to a nucleotide: • The sugar • The phosphate • The base • There are four different bases: • Adenine • Thymine • Guanine • Cytosine DNA Structure • The sugars and phosphates make up the sides of the ladder. • The bases make up the rungs. DNA Replication • When a cell divides, the DNA needs to be copied so that each new cell has a full set of DNA. • This process is called Replication. • A new cell is able to make any missing part it may need as long as it has a full copy of DNA.