* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microworlds Study Guide
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
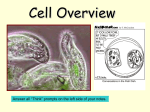
Microworlds Study Guide Anton Leeuwenhoek He was the first person to make and use over 240 microscopes. Leeuwenhoek lived in the 1600’s in the Netherlands. Most of his microscopes were very small, just 1”x2”. He was the first person to ever see one celled plants and animals. He discovered bacteria when he scraped plaque from his teeth. He also discovered that mammals have round blood cells while birds and fish have oval blood cells. Only 9 of Leeuwenhoek’s 240 microscopes remain today. Robert Hooke Robert Hooke lived in the 1600’s in England. One of the differences between Leeuwenhoek and Hooke was that Hooke drew what he saw under the microscope. Hooke invented the Barometer. Meteorologists use them to detect air pressure. Hooke also worked to improve microscopes. He learned that making the lenses MORE round makes them more powerful. Mounting Techniques Wet-mount: This is a technique using two flat slides and a drop of water. This process is used for flat objects like… fish scales hair feather leaf butterfly wing blood Well slide: This is a technique using a slide that has a depression in the center. This process is used for 3-Dimensional objects like… poppy seeds sponge Volvox pond water Volvox Commonly found in ponds. It is part of a group of organisms called green algae. A Volvox doesn’t have roots, stems, or leaves, but they are like green plants because they make their own food. This process is called photosynthesis. They live in a colony of 1,000 to 3,000 similar cells. The Volvox forms a sphere. They live in a jelly-like substance. Each cell has two tails called flagella. These tails are what move the Volvox through the water. It rolls like a ball. There are daughter colonies that split from the parent colony when they are big enough to begin their own Volvox colony. Blepharisma Commonly found in ponds. It is a single celled pear shaped organism. It has a rosy coloration. It usually eats bacteria, but if it eats other microbes it becomes a giant Blepharisma. The giant Blepharisma becomes a cannibal and eats its own kind. It is covered with tiny hairs called cilia. The cilia are used like paddles for swimming or to push food in its mouth. To reproduce, the Blepharisma splits itself in half to produce twins. This is called binary fission. Draw a diagram of binary fission in the space provided. Vinegar Eels The vinegar eel is a harmless round worm. It is about 2mm long. Its body is almost transparent and you can see some of their organs. Vinegar eels are made of many cells. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can digest food. It has a mouth and an anus. Females have their babies lined up inside of them by age. Vinegar eels are only found in unpasteurized vinegar. Pasteurization is a process where a liquid is heated to a very high temperature. This sterilizes the vinegar, which kills all the microbes. Identify the cell terms Cell Wall: the thick covering of a plant cell made from non-living fibers. Cell Membrane: a thin, living cell covering (lets gases in and out) Nucleus: the cell part that controls activities of other cell parts (the brain of the cell) Vacuoles: storage sacs in a cell (stores water & waste) Cytoplasm: the jelly-like fluid between the cell membrane and the nucleus. (jello) Chloroplasts: the green cell part that traps sunlight. (jellybeans) Mitochondria: the powerhouse of the cell that releases energy. All living things are made up of cells. Draw and label a plant cell You only need to know the six items that are labeled Draw and label an animal cell (include the key words that go with each cell term) How are plant and animal cells different? 1. Animals cells do not have a cell wall 2. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are used to help the plant cell make its own food. Volvox Blepharisma Vinegar Eels