* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 7 Information Evening Presentation
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
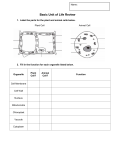
Year 7 Parents Success! School Students How does prepared look on a daily basis? • A readiness to learn and work - Fully equipped pencil case, including a ruler! - Scientific calculator - Arriving at lessons on time - Engaging with the starter activity - Interacting with the teacher and the rest of the class - Ensuring all homework is completed Conduct Managing Self Independence Critical Thinking Resilience How are we going to help and support your child? Knowledge Organisers (KOs),Learning Reviews, Homework and Marking Knowledge! Facts, information, and skills acquired through experience or education; the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject. 1. Knowledge Organisers • All students will receive Knowledge Organisers (KOs) for each subject. • These contain core knowledge, essential for progress in each curriculum area. • Students will be required to learn prescribed parts of the Knowledge Organiser every week. • They will be formally quizzed in the next lesson and there will be re-tests and intervention for students who underperform relative to their target. Knowledge Organisers The Benefits: - Teachers will be able to clearly see what an individual student knows or areas of the curriculum that need to be re visited. - Students will get used to revision and recalling, processing and applying information. - Evidence based studies show that regular testing boosts the capacity for retrieval. How to use your ‘Cells and Variation’ Knowledge Organiser Make sure that you are able to do the following tasks listed below. • Learn, Cover, Write, Check, Repeat! • Do this every day for 10 minutes. • Get someone to test you – or teach someone at home. • Create a mind map that makes links between all of the topics that you have learnt. Key Science Vocabulary Multicellular 1. Label a plant and animal cell with the correct organelles. Learn the function (job) of each organelle. Tissue 2. Learn the names of at least one specialised plant cell and one specialised animal cell. Explain how they are adapted to carry out their function (job). Chloroplast 3. Describe the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Explain how gases (eg oxygen) and nutrients (eg glucose) enter cells by diffusion. Membrane Spelling Practice Specialised Permeable Function Organ Cytoplasm Nucleus 4. Learn how vertebrates are classified according to their features. Understand the difference between a vertebrate and an invertebrate. 5. Be able to identify the cause of variation in a species – is it genetic or is acquired? Mitochondrion Classification Respiration Challenge: Investigate features of different invertebrate groups. What is meant by ‘survival of the fittest’ with reference to competition. How do the organs within a system eg. the digestive system, work together to carry out an overall function? Support – learn 3 spellings a week. Keep going back over the spellings you have learnt. Can you add in and learn the definitions too? Cell Cell membrane Cell wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Classification Cytoplasm Diffusion Genetic information Hooke (Robert) Living organism Microscope Mitochondrion Multicellular organism Nucleus Organ Organelle Photosynthesis Respiration Semi permeable Specialised Cell Tissue Unicellular organism Vacuole Variation A microscopic building block that makes up all organisms. An organelle. A cell covering that allows food, water and oxygen in. Lets waste out. It is semi-permeable (allows some things through but not others) An organelle. A cell wall is around the outside of the cell membrane. Maintains the rectangular shape of the plant cell. Made of cellulose. A substance. A green dye which absorbs sunlight. A plant organelle. Only found in plants. Photosynthesis (making food) happens here. Using common features to group animals and plants eg vertebrates/invertebrates, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibia, fish An organelle. A jelly-like liquid. Contains all other organelles. Where chemical reactions happen. The movement of gas particles or particles in solution from an area of high to low concentration eg oxygen diffusing into cells The instructions. Hold information about the organism's characteristics. Found in the nucleus. Discovered that living organisms are made out of microscopic building blocks that look like rooms, which he named 'cells'. Anything that can (MRS GREN) move, respire, (be) sensitive, grow, reproduce, excrete and (get) nutrition. Equipment. A tube containing lenses that can make microscopic objects like cells look larger. An organelle. Site of respiration. Releases energy. Plural: Mitochondria. An organism. Made up of many cells. E.g. ant, tree. An organelle. The control centre of the cell. Holds genetic information, to allow cell duplication. Plural: Nuclei. Made out of many types of tissue. E.g. stomach, lungs. Makes up a cell. A process. Happens in the chloroplast. Sunlight converts into sugar. A process. Happens in the mitochondrion. Oxygen and sugar convert into carbon dioxide and water (and energy). Allowing some substances through. A cell adapted for a particular function eg sperm, nerve, palisade, muscle cell A collection of the same cells, working together. E.g. epithelial tissue. An organism. Made up of one cell. E.g. amoeba. A plant organelle. Filled with sugary sap, water and waste. Differences in characteristics seen within and between species. These can be inherited (caused by genes) or acquired during a lifetime. Cells and Variation Animal cell Plant cell 2. Homework and what you can expect from us. • Each term: • A Knowledge Organiser with associated learning homework. • 2 extended pieces of writing per term, formatively marked (1 piece for foundation subjects). • 1 Learning Review (3 in Y7). • 1 Assessment, formatively marked. • Books are high quality notebooks – checked but not marked. 3. Learning Reviews A revision of components at the end of the course (often prior to KAs, end of unit, end of term etc). Structured review which will feature revision questions and tasks. Completion of notes which will serve as revision notes. Joined up 5 year approach to revision.