* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Levels of Organization
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
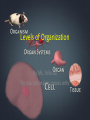
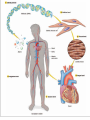
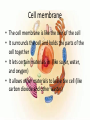
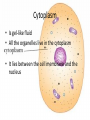
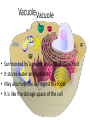
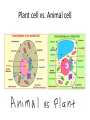
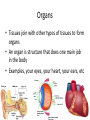
Levels of Organization By Ms. Vriksha ~for educational purposes only~ Cells • • • • Basic units of all living things Tiniest organisms are made of only single cells You need a microscope to see cells Most cells do the same things that you do to stay alive each day Cell functions • Cells take in food and get rid of wastes • They use materials in food to grow and repair wounds • Cells sense and respond to changes in their surroundings • They communicate and work with other cells Cell functions (cont’d) • • • • A few cells move All cells have parts inside them that move All cells need energy They get their energy through cellular respiration Cellular respiration • Cellular respiration is the combining of oxygen and food, such as sugar, to get energy Parts of a cell • Parts of a cell are called organelles Cell membrane • The cell membrane is like the skin of the cell • It surrounds the cell and holds the parts of the cell together • It lets certain materials in (like sugar, water, and oxygen) • It allows other materials to leave the cell (like carbon dioxide and other wastes) Cytoplasm • Is gel-like fluid • All the organelles live in the cytoplasm • It lies between the cell membrane and the nucleus Mitochondria • Is an organelle that change chemical energy of food into a form that the cell can use • It is called the “powerhouse of the cell” Ribosomes • Protein makers • Organelles that begin the process of making proteins Vacuole • • • • Surrounded by a membrane and contains fluid It stores water and nutrients May also help the cell digest the food It is like the storage space of the cell • Is like the “brain” of the cell • Directs all of the cell’s activities • It stores information that will be passed on to new cells Plant cells • Have all the parts found in the animal cells plus some parts not found in animal cells: 1. Chloroplast 2. Cell wall Chloroplast • Organelles that contain chlorophyll (green color pigment) • Plants make food when sunlight strikes chlorophyll Cell wall • A rigid cell wall outside the cell membrane • Gives the cell support Size and shape of cells • Cells need to be big enough for all of its parts • It needs to be small enough that oxygen and other materials can travel to all parts of the cell fast enough • The shape of the cell is determined by the job that cell does Plant cell vs. Animal cell Tissues • Tissues are groups of the same kind of cells that work together to do the same job • Muscle cells work together as a team to make muscle tissue Organs • Tissues join with other types of tissues to form organs • An organ is structure that does one main job in the body • Examples, your eyes, your heart, your ears, etc Organ Systems • Just like cells and tissues, organs also work together • An Organ system is a group of organs that work together to carry out a life process • Ex, your mouth, stomach, intestines and other other organs help you to digest food Receiving food and oxygen • Every cell needs a supply of food and oxygen and a way to get rid of wastes • In multicellular organisms, organ systems help the cells meet their needs • Digestive system takes in the food we need, then it breaks it down to a form that the cells can use • Substances in food needed by cells: NUTRIENTS Transport of nutrients and waste • In many animals blood transports nutrients to the cells • Blood is a tissue in the circulatory system • Blood also carries sugar and oxygen to cells • Blood also helps carry waste away form cells Coming Soon: Transportation of Materials in plants ~ a presentation by Ms. Vrisksha~ ~for educational purposes only~