* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit A, Chapter 1, Lesson 1
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
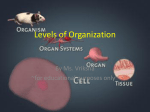
Unit A, “Processes of Living Things” Chapter 1, “From Single Cells to Body Systems” Lesson 1, “What Are Cells, and What Do They Do?” pgs. A6-A13 Cells A single square inch of human skin has more than ______19 million_________ cells. Within blood vessels there are two types of blood cells. Draw and label them. The first microscope was invented ____in the early 1600’s___________. In 1665, Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork through a microscope. He saw tiny walled spaces or tiny rooms, which he called ______cells_________. Define Cell – the basic unit of structure and function of all living things All plants and animals have what in common? They are all made up of cells Name three different types of cells. 1.White blood cells 2.Red blood cells 3.Muscle cells Parts of a Cell Even smaller structures in cells are called organelles. Define these plant and animal cell organelles: Cell Membrane – a thin covering that holds the parts of the cell together, it also separates the cell from its surroundings (skin) Nucleus – controls the cell’s activities (brain) Chromosomes – threadlike structure located in the nucleus, contains information about the characteristics of the organism Cytoplasm – jellylike substance Mitochondria – release energy from food (powerhouse/power plant) Vacuoles – storage for food, waste, or water What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not? What are their functions? Cell wall – gives the plant strength Chloroplasts – make food for the plant How Cells Move Define Diffusion – when particles of a substance move from an area where there are a lot, to an area where there are fewer Give an example of diffusion: Spraying perfume in the classroom, particles spread out so everyone smells aroma Passing gas in the classroom, particles spread out Define Osmosis – the movement of water and dissolved materials through the cell membrane Give an example of osmosis: If entire class tries to enter Mr. Moose’s classroom at same time through door (cell membrane), some make it in, some do not Tissues, Organs, and Systems Define Tissue – cells that work together to perform a specific function Name four kinds of tissues: 1.Nervous tissue 2.Muscle tissue 3.Connective tissue 4.Epithelial tissue Tissues that work together form an _____organ__________. Give an example of an organ: Lungs Liver Skin Define System – organs that work together Give an example of a system: Circulatory system Digestive system Remember: Cells working together form a ______tissue_________. ____Tissues___________ working together form an ________organ_______. _____Organs__________ working together from a ______system _________.