* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1 Lesson 1
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
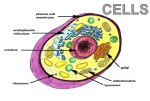
5th Grade-Chapter 1 Lesson 1- Cells VOCABULARY 1. organism2. cell3. unicellular4. multicellular5. chlorophyll6. tissue7. organ8. organ system- NOTES What are cells? Cells are the smallest unit of living things that can carry out the basic processes of life. Cells come from other cells. A cell divides, or splits, into two new cells. Unicellular-one-celled organism o Life processes include growing, responding to an environment, reproducing, and getting food. Multicellular-many-celled organism. o Ex: trees, frogs, and humans o Every cell carries out its own life process. o Cells work together to take care of different functions. Scientists estimate that there are more than 1 billion kinds of unicellular organisms. What is inside an animal cell? Your body has more than 200 different kinds of cells. Plant and animal cells have several basic structures called organelles. Organelles help cells perform life processes. They have functions that help keep cells alive. Cell Membrane o The layer around the outside of the cell. o Gives cell its shape. o Controls what materials move into and out of the cell. Cytoplasm o Gel-like liquid o Occupies the region from the nucleus to the cell membrane. o Made mostly of water. o Organelles float in the cytoplasm. o Supports cell structures. o Constantly moving through the cell in a stream-like motion. Nucleus o Cell’s control center. o Large, round organelle usually found in the center of the cell. o It has a membrane with pores, or openings, that allow certain materials to pass in and out. o Contains the master plans for all the cell’s activities. o Sends signals to other parts of the cell. o Controls the growth, movement, and division of cells. Mitochondria o Oval, membrane-covered organelles that supply energy for the cell. o Tiny power plant. o Break down food, which releases energy for cell use. o Cells that require a lot of energy usually have a great many mitochondria. Vacuoles o Membrane-covered structure used for storage. o Stores water, food, and wastes. o Can signal a vacuole to release whatever it is storing. o Some animal cells have many small vacuoles and some may not have any vacuoles. What is inside a plant cell? Plant cells have many of the same structures and organelles as animal cells. Plant cells often have a box-like shape and are a bit larger than animal cells. They have some additional organelles that animal cells do not have. Cell Wall o Additional outer covering around the outside of the cell. o Stiff structure outside the cell membrane. o Provides plant cell with strength and extra support. Vacuole o Plants cells have one large, central vacuole. o Stores excess water and provides extra support. o Extra water keeps the plant from drying out. Chloroplast o Where plants make their own food. o Green structure where the energy from sunlight is used to produce food fro the plant. o Green because they contain chlorophyll. o Plant cells that lack chloroplast are not green. o Found in the cells of leaves and stems of plants. How are cells organized? Unicellular- simple organization. o One cell that performs all life functions. Multicellular-specialized organization. o Different cells performing different functions. o Ex: muscles cells specialize in movement, red blood cells carry oxygen Cells working together form tissues. Tissues working together form organs. Organs working together form organ systems. o Ex: circulatory system, digestive system, nervous system. All of the cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems form an organism.