* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phagocytosis - mrswalmsley
Purinergic signalling wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
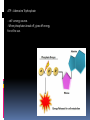
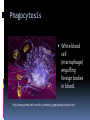
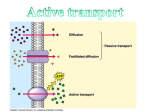
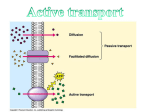
ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate - cell ‘s energy source. - When phosphates break off, gives off energy for cell to use. Active Transport Remember in passive transport, molecules move with the concentration gradient (from area of high [] to an area of low [] until they reach equillibrium. Sometimes the cell needs more than just an equal amount inside as outside Energy is used to pump molecules against the [] gradient Energy = ATP Example: digestion Food is eaten to obtain nutrients. Small intestine moves nutrients across its membrane and into the blood stream. Ex. Glucose – pumped across cell membrane using a carrier protein. ATP activates the protein to move glucose into the cell even though the concentration outside the cell is lower. Ex. Nerve and muscle cells sodium-potassium pump. Sodium and potassium are what allow messages to be sent between nerves. Messages = movement and function Bulk Transport Large amounts of material moving into or out of cell. Requires energy (ATP) Types: Endocytosis- movement of material into cell Phagocytosis : solids moving into cell Pinocytosis: liquids moving into cell Phagocytosis Solid particle comes into contact with cell membrane. Cell membrane moves around particle using pseudopods (“false feet”) and engulfs (swallows) particle. pseudopod Phagocytosis Once inside the cell, a lysosome fuses to the particle and uses its digestive enzymes to break down the particle. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Phagocytosis2.png Phagocytosis White blood cell (macrophage) engulfing foreign bodies in blood. http://www.peterjurek.com/rbv_site/web_pages/phagocytosis.html Exocytosis Reverse of endocytosis Movement of large particles out of the cell. Fig. 9 p. 71 of text http://www.cdli.ca/courses/biol2201 /unit01_org04_ilo01/b_activity.html Exocytosis Nerve cell transmission Activity at an axon terminal: Neuron A is transmitting a signal at the axon terminal to neuron B (receiving). Features: 1. Mitochondrion. 2. synaptic vesicle with neurotransmitters. 3. Autoreceptor. 4. Synapse with neurotransmitter released (serotonin). 5. Postsynaptic receptors activated by neurotransmitter (induction of a postsynaptic potential). 6. Calcium channel. 7. Exocytosis of a vesicle. 8. Recaptured neurotransmitter. http://www.thefullwiki.org/Axon_terminal