* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pseudopods
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
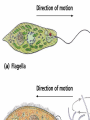
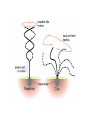
• These whiplike appendages extend from the surface of many types of eukaryotic cells. If there are many of them, they are called cilia; • if only one, or a few, they are flagella. Flagella also tend to be longer than cilia but are otherwise similar in construction. • Cilia and Flagella are hairlike organelles that branch out from the surface of the cell, where they help in the movement. These organelles can be found in any eukaryotic cells. Cilia are present when there are short and large numbers of organelles on the cell. Flagella are present when there are long and few numbers of organelles on the cell. • Pseudopods (which translates to "false feet") are temporary cytoplasm-filled parts of the cell wall that are able to change their form in order to move. They are used in some eukaryotic cells to move around or to eat. Most cells that do this are called amoeboids. The amoeba is a common example. • The cell wall makes a network of fibers. The cytoplasm flows into the network and fills it up, similar to a net filled with gelatin. This is able to move, lengthen, or shorten. The pseudopod extends from the amoeba. Then the main part of the amoeba flows into that pseudopod and the amoeba has changed its place. • Pseudopods are one of the three locomotion modes of unicellular organisms (together with flagella and cilia). Pseudopods can also capture prey by phagocytosis. Pseudopedia are used by some cells to move around. They can detect food and place it inside the cell. The human white blood cell uses this way to get around.