* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
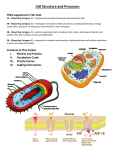
Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide Use the following materials to study for the exam: 1. Cytology – The Study of Cells Packet 2. Cell Membrane Packet (Passive Transport) 3. Active Transport 4. Outlining the Notes: Active Transport Using your notes on cell organelles, fill in the following chart: Cell Organelle Function Mitochondria Endoplasmic Reticulum Converts light energy into chemical energy Cell Wall Contains digest enzymes in order to get rid of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates Ribosomes Golgi Body What are three differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? 1. 2. 3. Animal, Plant, Both Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide In the Venn Diagram below, write down the differences and similarities between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells: Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Label the following parts of the eukaryotic cell: 1. Rough ER 2. Nucleus 3. Golgi Apparatus 4. Mitochondria Label the following parts of the eukaryotic cell: 1. Cell Wall 2. Central Vacuole 3. Chloroplast Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide Label the parts of a prokaryotic cell 1. DNA 2. Cytoplasm Why is having a small surface area good for a cell? ______________________________________________________________________________ Why is it good for the mitochondria and the chloroplast to have a LARGE surface area? _____________________________________________________________________________ Here is the cell membrane… 1. Label the parts of the cell membrane: A.) Phospholipid B.) Hydrophilic head C.) Hydrophobic tails 2. Use the diagram and your knowledge to answer the questions below Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide Which component of this membrane contains a hydrophobic region and acts as the primary barrier to MOST foreign substances? A. B. C. D. Protein Cholesterol Carbohydrate chain Phospholipid bilayer Facilitated diffusion uses which component of the cell membrane in order to move molecules into and out of the cell? A. Protein B. Cholesterol C. Carbohydrate Chain D. Phospholipid bilayer Living organisms can be classified as prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Which two structures are common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? A. Cell wall and nucleus B. Cell wall and chloroplast C. Plasma membrane and nucleus D. Plasma membrane and cytoplasm Using arrows show the movement of particles in the following images: Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide 1.) Passive Transport is when particles move from a ____________________ concentration to a _________________________ concentration, but active transport is when particles move from a ________________________ concentration to a ______________________ concentration. KIND OF LIKE WHEN YOU ARE RIDING A BIKE! Up a hill = ACTIVE TRANSPORT = requires energy! Downhill = PASSIVE TRANSPORT= no energy! 2. __________________ is when water molecules move through the cell membrane 3. Water always moves towards a ________________________ concentration of solutes and a ______________________ concentration of water. In the space provided draw the following: A hypertonic cell A hypotonic cell An isotonic cell Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide Using your knowledge of active transport, label the following types of based on the images provided. ______________________________ ___________________________ ____________________________________ A sodium-potassium pump within a cell membrane requires energy to move a sodium and potassium ions into or out of a cell. The movement of glucose into or out of a cell does not require energy. Which statement BEST describes the movement of these materials across a cell membrane? A. B. C. D. Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by osmosis. Sodium and potassium ions move by active transport, and glucose moves by facilitated diffusion. Sodium and potassium ions move by facilitated diffusion, and glucose moves by osmosis. Sodium and potassium ions move by facilitated diffusion, and glucose moves by active transport.