* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Division - AKNS Students Blogspot
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
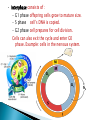
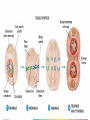
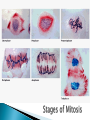
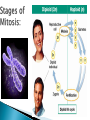
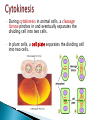
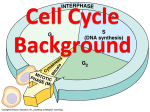
When a cell is not dividing, the DNA is in the form of a threadlike material called chromatin. When a cell is about to divide, the chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Chromosomes are structures in the nucleus made of DNA and protein. • Describe the events of cell division in prokaryotes. • Name the two parts of the cell that are equally divided during cell division in eukaryotes. • Summarize the events of interphase. • Describe the stages of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. • Explain how cell division is controlled. Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce themselves. • Cell Cycle – The cell cycle is the repeating set of events in the life of a cell. – The cell cycle consists of cell division and interphase. – Cell division in eukaryotes includes nuclear division, called mitosis, and the division of cytoplasm, called cytokinesis. • Interphase consists of : – G1 phase offspring cells grow to mature size. – S phase cell’s DNA is copied. – G2 phase cell prepares for cell division. Cells can also exit the cycle and enter G0 phase. Example: cells in the nervous system. • During cytokinesis in animal cells, a cleavage furrow pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell into two cells. • In plant cells, a cell plate separates the dividing cell into two cells. • Cell division in eukaryotes is controlled by many proteins. • Control occurs at three main checkpoints.