* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle Background
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
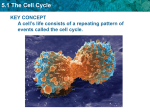
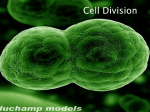
Most cells are less than 100 micrometers in diameter Cells are small! What are the benefits of small cells? Cells can easily supply nutrients and expel waste Molecules can be transported around and through the cell Cells need small size for simple communication with other cells and within themselves What do cells do to maintain their size? When a cell becomes too large it will either stop growing or divide. The cell cycle explains the process of division. Cells reproduce by a cycle of growing and dividing called the cell cycle A cell will spend most of its time in interphase During interphase the cell grows, develops, duplicates it’s DNA, and prepares to divide The stages of interphase are: G1, S, and G2 (Gap 1) G1 This is the period immediately after cell division. During this time: The cell grows, carries out normal functions, and prepares to replicate it’s DNA Synthesis (S phase) The cell will copy its DNA in order to prepare for cell division. Gap 2 (G2) The period when the cell prepares to divide the nucleus. The cell will take inventory to make sure that it is prepared for mitosis After interphase, follows mitosis and cytokinesis Mitosis The purpose is to divide the cell’s nucleus Cytokinesis The purpose is to divide the cell into two identical daughter cells