* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytology
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
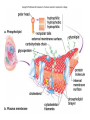
Cytology Biochemistry – Chap. 2 Cell Biology – Chap. 3 Learner Outcomes: • To describe the characteristics and identify the monomers of lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids and to define their role in biochemical processes. • To analyze and explain the chemical reactions the provide energy for the body. • To investigate and describe the integration of the chemical and physical properties that contribute to homeostasis in cells. • To compare the structures and functions of organelles within cells of the body. • To describe the processes involved in the cell cycle. Eukaryotic Cells • With the exception of symbiotic and parasitic relationships with bacteria, all of the cells of our body are eukaryotic. • What does this mean? Eukaryotic Cells • Plasma membrane • Nucleus and Nucleolus • Cytoplasm containing organelles • Each of our bodies exhibits specialization. The presence or absence of some organelles and their arrangements vary dependant on the needs of the cell. Fig. 3.2 Cellular Homeostasis – the plasma membrane • Semi-permeable or Selectively permeable • 2 methods used in crossing the membrane – active and passive • Active transport requires the use of ATP. Which organelle provides this high-powered molecule for the cell? • Passive transport uses the principles of diffusion to cross the membrane and does not require the use of ATP.