* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure and Function Notes #1
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
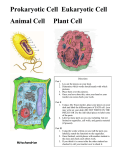
Structure and Function Notes #1 SF1, SF2, & SF3 SF1- Cell Theory • The cell theory states: • 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells. (If it is living it is made of cells.) • 2) The cell is the basic unit of all living things. (The cell is the building block for all parts of an organism.) • 3) All cells come from existing cells. (All cells are made by other cells.) SFK2- Cell structure-Animal Cell SFK2- Cell structure- Plant Cell SF2-Cell structure • The main difference in the structure of plant and animal cells are: • 1) Plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not. • 2) Plant cells have a very large and centrally located vacuole and animal cells have small vacuoles. • 3) Plant cells have chloroplasts and animal cells do not. • 4) Plant cells are generally much larger than animal cells. SF3- Whole cell function • There are two main types of cells: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. • Prokaryotes do not have membrane bound organelles; their DNA is floating in the cytoplasm. (Bacteria) • Eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles and their DNA is enclosed inside of the nucleus. (Plant and Animal cells) SF3- Whole cell function • In the cytoplasm of animal cells there are numerous protein filaments that give shape and support to the cell called the cytoskeleton. (like our skeletal system) • The cytoskeleton is also involved in cellular movement and parts/materials moving inside of the cell. • There are four major types of molecules in living organisms: Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates and Nucleic acids. Nutrient/Molecule Function Protein Used to build, repair and regulate processes. Proteins called enzymes help to chemical processes happen in cells. Lipid Fat molecules that do not mix with water and are used to store energy. Carbohydrate Used as a source of energy. Nucleic acid Carries information for the cell to make proteins. • The cell membrane is a very important structural component of cells. • The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that is interspersed with proteins. • The cell membrane regulates what goes in and out of the cell, which helps to maintain homeostasis or balanced, stable conditions in the cell. SF3- Whole cell function • Cells have to maintain a small size in order to function efficiently. • If cells get to large the rate of diffusion and osmosis would not be adequate and the cell would die. • Homeostasis is maintained by a combination of passive and active transport. • Passive transport requires no energy or action from the cell. Examples of passive transport are diffusion and osmosis. • Diffusion is materials transporting across a barrier due to concentration differences. • Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that only happens with water. • Active transport results from proteins actively “pumping” materials across a barrier, usually against a concentration gradient. • Sugars and other essential nutrients/materials needed in the cell are transported actively through protein “pumps” or gates in the cell membrane. SF4- Organelle function • Animal only organelle: Lysosomes- Produces enzymes that digest wastes, cell parts and foreign invaders. • Plant only organelles: Cell wall- Rigid outer structure of plant cells that shapes and supports the cell. Chloroplasts- contain chlorophyll and is the site of photosynthesis. • Organelles in both plant and animal cells: • Cell membrane • Cytoplasm- the fluid/gel that holds everything inside of the cell membrane. • Nucleus- membrane bound organelle that holds all of the DNA (a type of nucleic acid) • Golgi complex- packages and distributes materials within the cell. • Mitochondria- Site of cellular respiration where food products are broken down chemically into usable energy for the cell. • Ribosomes- the organelle responsible for building proteins by chaining together amino acids (building blocks of proteins). • Vacuoles- membrane bound, fluid filled organelles responsible for maintaining water levels inside of the cell. • Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum- A series of membranes that assists in the production and transporting of proteins. • Smooth ER- makes lipids and breaks down toxic materials.