* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
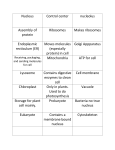
Looking Inside Cells 7th grade science Cells are small but there are even smaller structures inside a cell. These tiny structures are called organelles, and they carry out specific functions within the cell. Just as your stomach, lungs, and heart have different functions in your body, each organelle has a different function within the cell. Enter the Cell! Before you get into a cell you have to pass through the cell wall and the cell membrane! Animal cell Plant cell Cell Wall – (is ONLY in plant cells!) is a rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms - a plant’s cell wall helps to protect and support the cell The cell wall is made mostly of a strong material called cellulose – although the cell wall is tough, materials like water and oxygen can pass through it easily! The next barrier you must cross is the… Cell Membrane – controls what substances come into and out of a cell – everything the cell needs, from food to oxygen, enters the cell through the cell membrane and harmful waste products leave the cell through the cell membrane! ALL cells have cell membranes! In cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is located just inside of the cell wall. In other cells, the cell membrane forms the outside boundary that separates the cell from its environment Sail On to the Nucleus! Inside the cell, a large, oval structure comes into view, which is the nucleus! Nucleus – acts as the “brain” of the cell – you can think of the nucleus as the cell’s control center, directing all of the cell’s activities Nuclear Envelope – is the membrane that surrounds the nucleus and it protects the nucleus – materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in the nuclear envelope Chromatin – contain genetic material, the instructions for directing the cell’s functions – this is how the nucleus “knows” how to direct the cell Ex: instructions in the chromatin ensure that leaf cells grow and divide to form more leaf cells nucleus Nucleolus Nucleolus – located inside of the nucleus, where ribosomes are made Organelles in the Cytoplasm! As you leave the nucleus, you find yourself in the cytoplasm, the region between the cell membrane and nucleus! Cytoplasm – the region between the cell membrane and nucleus and its clear, thick, gel-like fluid – the fluid is ALWAYS moving! Mitochondria – rod-shaped structures that are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they convert energy in food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions Endoplasmic Reticulum – is a maze of passageways! The passageways carry proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another Ribosomes – some are attached to the surface of the ER (endoplasmic reticulum) and some float around in the cytoplasm, but ribosomes function as factories to produce proteins – from the ER, the proteins produced from the ribosomes, will be transported to the Golgi bodies! As you leave the ER, you see a structure that looks like flattened sacs and tubes! Golgi Bodies – receive proteins and other newly formed materials from the ER, package them, and distribute them to other parts of the cell – Golgi bodies also release materials outside the cell Chloroplasts – (are ONLY in plant cells!) capture energy from sunlight and use it to produce food for the cell – chloroplasts make leaves green! chloroplast Vacuoles – are used as storage areas of cells. They store food and other materials needed by the cell, and even waste products, too – most plant cells have one large vacuole, some animal cells do not have vacuoles, some do. Lysosomes – are small, round structures containing chemicals that break down certain materials in the cell – some chemicals break down large food particles into smaller ones. They also break down old cell parts and release the substances so they can be used again Specialized Cells! Plants and animals contain many cells. The cells are often quite different from each other and are specialized to perform specific functions Ex: Nerve cells are specialized to transmit information from one part of your body to another, and red blood cells carry oxygen throughout your body In many-celled organisms, cells are often organized into tissues, organs and organ systems! Tissue – a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function - your brain is made mostly of nervous tissue, which consists of nerve cells Organ – is made of different kinds of tissues that function together - your brain is made up of nervous tissue, and other kinds of tissue that support & protect it Organ System – is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function your brain is part of your nervous system, which directs body activities/process http://www.oum.ox.ac.uk/thezone/an imals/life/respire1.htm Go to this site to learn more!