* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure and Function
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
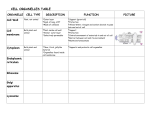
Cell Structure and Function Textbook: Chapter 6 What you need to know! • The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. • The structure and function of organelles common to plant and animal cells. • The structure and function of organelles found only in plant cells or only in animal cells. • How chloroplasts and mitochondria evolved through endosymbiosis (Endosymbiotic Theory) 1. Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes 1. Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Prokaryotes Bacteria Single celled Eukaryotes Animal cells, plant cells, fungi, protists Mostly multi-cellular No membrane bound organelles membrane bound organelles Very small 100x bigger 4 byo 3 byo (Endosymbiotic Theory) Chromatin Naked DNA Both have: • Plasma membrane • Cytoplasm • DNA • Ribosomes This is the minimum requirement for living cells 2. Cell organelles vs cell structures Definition: A true organelle is surrounded by one or more membranes Single membrane bound organelles: • Golgi • ER • Vacuole • Lysosome, Peroxisomes • Cilia, Flagella 2. Cell organelles vs cell structures Double membrane bound organelles: • Nucleus (N) • Mitochondria (M) • Chloroplasts (C) Endosymbiotic Theory States that M & C were prokaryotic organisms that were swallowed by another larger prokaryote 3-4 byo through a process called endocytosis. M & C were not digested but formed a: mutualistic symbiosis with their host. Endosymbiotic Theory Arguments that support ET 1. M, C, and N have their own DNA 2. M and C DNA is similar to prokaryotic DNA 3. M and C multiply independent from nucleus/mitosis 4. M, C, and N have double membranes Cell structures that are not real organelles • • • • • Ribosomes Membranes Plasms Centrioles Cytoskeleton 3. Cytoskeleton • • • • Network of elastic fibers Made of proteins Found in eukaryotes Used for cell shape, movement, anchoring and movement of organelles, mitosis Microfilaments 3. Cytoskeleton Intermediate Filament Microtubule Microfilaments Intermediate Filaments Microtubule Size small medium large Protein subunits actin keratin tubulin Characteristics Tension resistant Tension resistant Compression resistant Functions Muscle contraction, Makes cytoplasm gel-like, amoeba movement Permanent role in cytoskeleton nucleus anchor Grow out of centrosome Easy assembly/ Disassembly Attachment of Organelles Sliding tracks For organelles Separate Chromosomes in Mitosis Cilia and Flagella 4. Endomembrane System Large membrane system that spans entire cell, makes up for over 50% of cell’s entire membrane, used for transport, secretion, compartmentalization: nuclear envelope, ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vesicles (membrane bound, liquid filled spheres) a) Directly connected through touching membranes: nuclear envelope and ER b) Indirectly connected through migrating vesicles: ER with Golgi, Golgi with Plasma Membrane Secretion of Proteins • Examples: mammary cells milk, pancreas insulin • Rough ER (rER) - ribosomes on rER make polypeptide chains that grow inside lumen (space inside ER) Secretion of Proteins • Vesicles from rER pinch off, migrate to and fuse with Golgi, forming side (cis) • Golgi – finishes proteins • Packed into vesicles pinching off the maturing side (trans) • Vesicles migrate and fuse with plasma membrane – exocytosis Secretion of Lipids • Smooth ER: lipids for milk secretion, sex/steroid hormones, cholesterol Inner workings of the cell • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zrXykvo rybo&feature=player_embedded