* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture notes-metabolism pathways-web
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
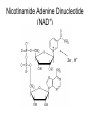
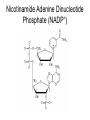
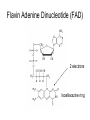
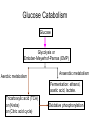
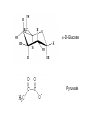
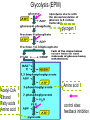
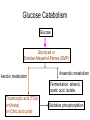
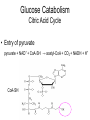
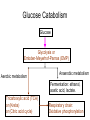
Metabolic Pathways - Overview of metabolism pathways - Bioenergetics - Metabolism: - Glucose catabolism - aerobic pathway - anaerobic pathway - Hydrocarbon - Nitrogen compounds - Photosynthesis - Overview of biosynthesis Metabolic Pathways - Overview of metabolism pathways Metabolism: - Catabolism: The intracellular process of degrading a compound into smaller and simpler products and generating energy. Glucose to CO2, and H2O, protein to amino acids. - Anabolism: the synthesis of more complex compounds and requires energy. Synthesis of glycan (polysaccharide), DNA, RNA, and lipid. Metabolic Pathways - Overview of metabolism pathways - Categories: Degradation of nutrients: carbohydrate, nitrogen compounds, lipids and nucleic acids. Biosynthesis of small molecules, such as building blocks for biopolymers. amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids and sugars Biosynthesis of large molecules glycan, glycogen, lipids and nucleic acids. Major Metabolic Pathways - Overview of metabolism pathways Metabolic Pathways - Overview of metabolism pathways End products are formed and released from the cells through these reactions, which are often valuable products for human or animal consumption. ethanol, amino acids, enzymes, fatty acids, antibodies. Metabolic Pathways - Bioenergetics - Energy is mainly stored or transferred by adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Other energy carrying compounds include GTP, UTP and CTP. Metabolic Pathways - Bioenergetics - Transfer of biological energy from high-energy to low energy compounds via ATP or its analog compounds. Metabolic Pathways - Bioenergetics - Reducing power: supply hydrogen atom in biosynthesis. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NADH) Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FADH2) NADH and FADH2 are major electron carriers in the oxidation of fuel molecules and for ATP generation. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH). major electron donor in reductive biosynthesis Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) 2e- , H+ Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP+) Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD) 2 electrons Isoalloxazine ring Review of Metabolism Pathways http://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway/map/map01100.html Glucose metabolism is the centre of the cell metabolism pathways Glucose Catabolism Glucose Glycolysis or Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) Aerobic metabolism Anaerobic metabolism Fermentation: ethanol, acetic acid, lactate. Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or (Krebs) or (Citric acid cycle) Oxidative phosphorylation Glucose Catabolism Glycolysis • Glycolysis or Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) Breakdown of a molecule of glucose to two pyruvate molecules. - Each pathway is catalyzed by particular enzyme(s) - Generating 2 ATP, 2 NADH and 2 pyruvate (Key Metabolite). - Taking place in cytoplasm a-D-Glucose Pyruvate Glucose Catabolism Glycolysis • http://www.gwu.edu/~mpb/glycolysis.htm • http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/glycolysis .html (animation) Glycolysis (EPM) glycogen Amino acid Acetyl-CoA Ethanol Fatty acids Amino acid control sites: feedback inhibition Glucose Catabolism Glycolysis • The overall reaction in glycolysis is: Glucose + 2ADP + 2 NAD+ + 2 Pi →2 pyruvate + 2 ATP+ 2 (NADH + H+) Glucose Catabolism Glucose Glycolysis or Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) Aerobic metabolism Anaerobic metabolism Fermentation: ethanol, acetic acid, lactate. Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or (Krebs) or (Citric acid cycle) Oxidative phosphorylation Glucose Catabolism Krebs, Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA), or Citric Acid Cycle • Under aerobic conditions • Taking place - in mitochondria in eucaryotes - associated with membrane-bound enzymes in procaryotes • Pyruvate produced in glycolysis (EMP) pathway transfer its reducing power to NAD+. Glucose Catabolism Citric Acid Cycle Roles: • Provide electron (NADH) for the electron transport chain for ATP generation and biosynthesis • Supply C skeletons for amino acids synthesis Glucose Catabolism Citric Acid Cycle • Entry of pyruvate pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA-SH → acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+ CoA-SH Glucose Catabolism Citric Acid Cycle • One molecule of acetyl-Co-A generates: 3 (NADH+H+), FADH2, GTP, and 2CO2 amino acid synthesis Control site NADH generated CO2 released FADH2 generated Citric Acid Cycle amino acid synthesis http://www.gwu.edu/~mpb/citric.htm http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/krebs.html Glucose Catabolism Citric Acid Cycle The overall reaction of TCA cycle: acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD + FAD + Pi + 2H2O → CoA + 3(NADH + H+) +FADH2+GTP+ 2CO2 • Intermediate products such as oxylacetate and α–ketoglutarate are used as precursors for the synthesis of certain amino acids. • The reducing power (NADH + H+ and FADH2) is used for biosynthesis pathway or for ATP generation through the electron transport chain. Glucose Catabolism Glucose Glycolysis or Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP) Aerobic metabolism Anaerobic metabolism Fermentation: ethanol, acetic acid, lactate. Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or (Krebs) or (Citric acid cycle) Respiratory chain: Oxidative phosphorylation