* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download answers - Biology Resources
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Chromatophore wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
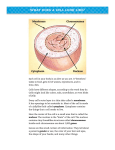
TEACHERS’ NOTES Diffusion 5.03 Experiment 5 Discussion – answers 1 There should be no escape of pigment in tube 30. Tube 70 should have a deep red colouration. 2 The red pigment does not diffuse out of the cell at 30oC but it does so at 70oC. 3 The cytoplasm and nucleus are composed of living material. Cell sap and the cellulose cell wall are not living materials. 4 High temperature kills most living materials (by denaturing their proteins, e.g. enzymes and structures in the cell membrane). 5 It seems likely that a living process in the cytoplasm controls the diffusion of the pigment. Diffusion of pigment is prevented when the cytoplasm and cell membrane are intact but not when they are ‘killed’. Students may suggest that the nucleus is the controlling factor since they have learned that the nucleus controls processes in the cell. If this were the case, the intact nucleus would have to influence some process in the cytoplasm, making it impermeable to the red pigment.